The second USACO contest of the 2016-2017 season has started and will end on Jan 16 at 23:59 UTC-12 time.
Let's discuss the problems here after the contest :)
→ Обратите внимание
До соревнования
Codeforces Round 940 (Div. 2) and CodeCraft-23
2 дня
Зарегистрироваться »
Codeforces Round 940 (Div. 2) and CodeCraft-23
2 дня
Зарегистрироваться »
*есть доп. регистрация
→ Лидеры (рейтинг)
| № | Пользователь | Рейтинг |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ecnerwala | 3648 |
| 2 | Benq | 3580 |
| 3 | orzdevinwang | 3570 |
| 4 | cnnfls_csy | 3569 |
| 5 | Geothermal | 3568 |
| 6 | tourist | 3565 |
| 7 | maroonrk | 3530 |
| 8 | Radewoosh | 3520 |
| 9 | Um_nik | 3481 |
| 10 | jiangly | 3467 |
| Страны | Города | Организации | Всё → |
→ Лидеры (вклад)
| № | Пользователь | Вклад |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | maomao90 | 174 |
| 2 | awoo | 164 |
| 2 | adamant | 164 |
| 4 | TheScrasse | 159 |
| 4 | nor | 159 |
| 6 | maroonrk | 156 |
| 7 | -is-this-fft- | 150 |
| 8 | SecondThread | 147 |
| 9 | orz | 146 |
| 10 | pajenegod | 145 |
→ Найти пользователя
→ Прямой эфир
Codeforces (c) Copyright 2010-2024 Михаил Мирзаянов
Соревнования по программированию 2.0
Время на сервере: 19.04.2024 13:39:28 (j3).
Десктопная версия, переключиться на мобильную.
При поддержке
Списки пользователей

| Название |
|---|









Bringing it back to recent actions
Is it possible that I submit my solution even thought I have already competed for 4 hours? Of course this submission will be out of competition.
This sounds convincing, I think. You will be able, but after the contest ends for everyone.
OK, thank you.
How to solve "Building a Tall Barn" and "Subsequence Reversal" from Platinum?
Wait until 16:00 UTC today when the contest ends for everyone.
Really sorry. I thought contest has already ended since it marked ended in clist.by.
This is something repeated every contest... opened an issue for it there.
Fixed.
Its still on for me, I got 10 minutes left :P Got AC on problems 1 and 2 only :/
I was trying this for the third one (couldn't debug in time, ended up with 6/10): note that instead of saying "reverse a subsequence", you could say "select a bunch of pairs of indices such that for any two pairs one of them is contained within the other and swap the values of each pair". Now let DP(l, r, p, q) denote the answer of the subarray (l, r) given that the lis lies within the range (p, q). From (l, r) you can go to either (l+1, r), (l, r-1), (l+1, r-1), or swap a[l] and a[r] and then go to (l+1, r-1).
Did anyone get ac with this approach?
Yes, I did.
You can calculate each state in either O(n^2), O(n), or O(1). Anything faster than O(n^2) works, but I did it in O(1). Also, I did it recursively, and I'm sure than a huge number of states were never reached in the computation.
I did it in O(n^2) and get full score. Less than 1 sec in max test. How did you manage to compute the dp in O(1)?
I was computing the transitions in O(1). DP(l, r, p, q) is the maximum of the following values:
Yup, I basically did it like this too.
You've forgotten about the two cases where we do swap the values a[l] and a[r], but only use one of them in the sequence, e.g.:
An example of such a sequence would be 3 1 2 100 4 5 6 7 8. Swapping the 3 and the 100 will give you an optimal sequence of length 8.
How did you solve 2 (platinum). I did this with n ternary searches inside the binary but it TLE, because it was . After some thinking I removed the ternary and replaced it with a derivative so the final solution became
. After some thinking I removed the ternary and replaced it with a derivative so the final solution became 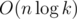 . It passed but I wasted like 2.5 hours on this. So my question is. Is there an easier solution (or actually what is the easy solution)?
. It passed but I wasted like 2.5 hours on this. So my question is. Is there an easier solution (or actually what is the easy solution)?
code: http://ideone.com/ojPGlI
PS: sorry for the early post
FFS I WROTE IT JUST ABOVE, 16:00 UTC, DO YOU NOT HAVE A CLOCK ONLINE?!!!1!
My solutions, short:
HLD trick where I bruteforce over all subtrees of smaller sons and use BIT for the subtree of the largest sons. It needs one more precomputational pass where I don't use the BITs, but figure out which numbers will be in them so that I could compress them.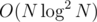 .
.
code
In real numbers,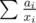 with the constraint
with the constraint 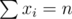 has a minimum at
has a minimum at 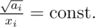 . I thought it would be sufficient to use this as an estimate (take the lower bound, but at least 1 cow) and then greedily add a remaining ≤ N cows in order to minimise the time.
. I thought it would be sufficient to use this as an estimate (take the lower bound, but at least 1 cow) and then greedily add a remaining ≤ N cows in order to minimise the time.
I failed the last test case only... so I added a better greedy where I look at the smallest time I can lose by removing 1 cow, the largest time I can gain when adding 1 cow somewhere, and as long as more is gained than lose, remove and add a cow accordingly. It can be implemented with a set<>; if there are T such remove/add steps, the time complexity is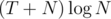 .
.
code
DP over subarrays with states (start, end, max. number on the left, min. number on the right). O(N4).
code
UPD: I see a lot of downvotes. CF comments as usual.
They are probably because your spoilers were empty until a couple of minutes ago. I like your solutions, but don't understand what you're saying about the first problem. Why would you need anything that has anything to do with HLD?
My solution was with the "merging sets" trick, but a set can't answer a query "how many numbers are there smaller than x" so I essentially made n segment trees and for each vertex merged the segment trees of its children.
EDIT: removed second solution, I got something wrong;
Lol why would I post solution when the contest was running? :D And I did say "short". Very, very short. But I got a lot of downvotes after they weren't empty.
I call it HLD trick because you're basically building BITs over HLD, although not building or using the HLD paths directly. You can do the same with segtrees and with BITs, but you need to build them first, in that precomputation pass, and then, you can merge only the elements from the trees for the smaller sons into the largest one.
Okay, I get it now, thank you. :)
We basically did the same thing, but I didn't precompute these paths. Instead every vertex chose its biggest child's tree as its own, and merged all the other seg-trees into it.
After flattening the tree, problem 1 can be solved with a merge sort tree. We keep a vector in each node of a segment tree that contains the relevant range sorted. For querying, we can binary search in current node to find the count of numbers greater than some x. Space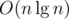 and time
and time 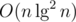 .
.
I realized that if k was small, the greedy algorithm above did not work. So if k <= 10^7, I set all b[i] = 1, otherwise I did the above algorithm, and it got AC.
Problem 1 can be solved much simpler in O(NlogN).
Yeah, good point. What I wrote was just the first thing that came into my mind.
please, be careful in future for telling these "first things"
For tallbarn, you're given a sequence a and asked to minimize the sum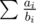 subject to
subject to 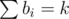 . Suppose
. Suppose 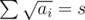 . We have a lower bound from a consequence of Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, mostly known as Titu's lemma (I wrote an article here)
. We have a lower bound from a consequence of Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, mostly known as Titu's lemma (I wrote an article here)
$o$ with equality when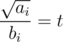 for some constant t. But
for some constant t. But 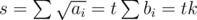 implies
implies 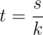 . So we can set
. So we can set 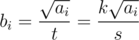 and achieve the minimum value
and achieve the minimum value 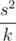 . But bi values have to be positive integers, so the sequence b has to be adjusted. First off we should make all bi < 1 equal to 1.
. But bi values have to be positive integers, so the sequence b has to be adjusted. First off we should make all bi < 1 equal to 1.
At this step I greedily adjusted the sequence in two ways and took the minimum.
Firstly I replaced bi with ⌊ bi⌋ for all i. Then the new total sum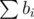 is less than k and the target value has increased. We can add the extra values in a way that the sum will be minimized. If we add 1 to bj for some j then the sum decreases by
is less than k and the target value has increased. We can add the extra values in a way that the sum will be minimized. If we add 1 to bj for some j then the sum decreases by
so pairs (ai, bi) get priority based on this value. We can add all pairs in a priority queue, keep increasing top elements and push them again till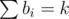 again.
again.
Secondly, I replaced bi with ⌈ bi⌉ for all i and did something similar to above. This time the sum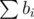 will be greater than k and we can delete extra values keeping another priority queue.
will be greater than k and we can delete extra values keeping another priority queue.
Finally take the minimum from these two adjustments.
Code: http://ideone.com/gItN6P
.
Actually, in reals,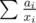 with the constraint
with the constraint 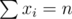 has its minimum at
has its minimum at 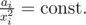 from Lagrange multipliers (or simply taking derivatives when all but two variables are fixed).
from Lagrange multipliers (or simply taking derivatives when all but two variables are fixed).
I use Simulated Annealing method on third task and get OK :)
How does it work here?
my code
I like your idea, you didn't bother in implement lis in O(nlogn) :) Nice approach. +1
Can you explain your method in a bit more detail? I haven't heard of simulated annealing, and would like to learn more about it.
Also, what sorts of problems does one use simulated annealing on?
when n is small and you need to minimaze/maximaze some function you can use Simulated Annealing method. like this task
i know only where to read about this method in russian, sorry:( i think you can google it and find some information about it.
Can you give the link of that russsian article?
article by KOTEHOK
In P2, you can solve with binary search.
Define f(x, i) to be the time you can cut off if room i currently has x cows, and you place one more. Then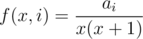 . You can binary search D such that all rooms have f(x,i)<=D, which you can solve with some quadratic formulas. Complexity is O(n log K)
. You can binary search D such that all rooms have f(x,i)<=D, which you can solve with some quadratic formulas. Complexity is O(n log K)
Your LaTeX is slightly messed up.
Anyways, what I really wanted to say, your username is really nice, especially appropriate for the tree problem you proposed P1 for the USACO contest. (Is it you?)
BTW, to whom you send nodes?
No, that guy is some doppelganger who wants to take my name. Really, i am just some poor guy who just sends nodes, particularly segtree ones because low cost :)
How do you make sure the sum of the x's is equal to K?
That's the transition of the binary search: if sum of x's is more than K, try higher differences, else try lower differences.
If I'm not mistaken I've achieved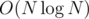 in Platinum 1.
in Platinum 1.
First, I compressed values in interval {1, ...N}. Then, put all nodes with their discovery time and finish time in one array, along with values of nodes, and sorted them by position. Finally, by iterating through that array and updating BIT, made solution for every node.
Code.
Does this work for platinum 1st problem?
Firstly build eulerian tour over tree. Now sort cows by p. Answer for cow v is (sum on segment [l[v], r[v]]) / 2, and after that add position l[v] and r[v] 1.
Is there any way to submit now? I optimised P2 a bit but time was up!!
After the results are published, problems are moved to practice.
Where can I find problems? http://usaco.org/index.php?page=contests have only problems till first contest
Read the comments here before asking.
Results are now available.
http://usaco.org/index.php?page=jan17results