Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define forn(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < int(n); i++)
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<string> a(n), b(n);
forn(i, n) cin >> a[i];
forn(i, n) cin >> b[i];
map<string, int> cnta, cntb;
forn(i, n) ++cnta[a[i]];
forn(i, n) ++cntb[b[i]];
int ans = n;
for (auto it : cnta) ans -= min(it.second, cntb[it.first]);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, M;
vector<int> a;
inline bool read() {
if(!(cin >> n >> M))
return false;
a.assign(n, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
return true;
}
vector<int> f[2];
inline void solve() {
a.insert(a.begin(), 0);
a.push_back(M);
f[0].assign(a.size(), 0);
f[1].assign(a.size(), 0);
for(int i = int(a.size()) - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
f[0][i] = f[1][i + 1];
f[1][i] = (a[i + 1] - a[i]) + f[0][i + 1];
}
int ans = f[1][0];
for(int i = 0; i + 1 < int(a.size()); i++) {
if(a[i + 1] - a[i] < 2)
continue;
int tp = (i & 1) ^ 1;
int pSum = f[1][0] - f[tp][i];
ans = max(ans, pSum + (a[i + 1] - a[i] - 1) + f[tp][i + 1]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
if(read())
solve();
return 0;
}
1000C - Подсчет покрытых точек
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector<pair<long long, long long>> a(n);
vector<long long> cval;
for (auto &i : a) {
scanf("%lld %lld", &i.first, &i.second);
cval.push_back(i.first);
cval.push_back(i.second + 1);
}
sort(cval.begin(), cval.end());
cval.resize(unique(cval.begin(), cval.end()) - cval.begin());
vector<int> cnt(2 * n);
for (auto &i : a) {
int posl = lower_bound(cval.begin(), cval.end(), i.first) - cval.begin();
int posr = lower_bound(cval.begin(), cval.end(), i.second + 1) - cval.begin();
++cnt[posl];
--cnt[posr];
}
for (int i = 1; i < 2 * n; ++i)
cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
vector<long long> ans(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < 2 * n; ++i)
ans[cnt[i - 1]] += cval[i] - cval[i - 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%lld ", ans[i]);
puts("");
return 0;
}
1000D - Очередная задача на подпоследовательности
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1009;
const int MOD = 998244353;
int n;
int a[N];
int dp[N];
int C[N][N];
int main() {
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){
C[i][0] = C[i][i] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j < i; ++j)
C[i][j] = (C[i - 1][j] + C[i - 1][j - 1]) % MOD;
}
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
dp[n] = 1;
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i){
if(a[i] <= 0) continue;
for(int j = i + a[i] + 1; j <= n; ++j){
dp[i] += (dp[j] * 1LL * C[j - i - 1][a[i]]) % MOD;
dp[i] %= MOD;
}
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
sum += dp[i];
sum %= MOD;
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 500043;
vector<int> g[N];
vector<int> t[N];
int tin[N], tout[N], fup[N];
int p[N];
int T = 1;
int rnk[N];
vector<pair<int, int> > bridges;
int st;
int d[N];
int n, m;
int get(int x)
{
return (p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = get(p[x]));
}
void link(int x, int y)
{
x = get(x);
y = get(y);
if(x == y) return;
if(rnk[x] > rnk[y])
swap(x, y);
p[x] = y;
rnk[y] += rnk[x];
}
int dfs(int x, int par = -1)
{
tin[x] = T++;
fup[x] = tin[x];
for(auto y : g[x])
{
if(tin[y] > 0)
{
if(par != y)
fup[x] = min(fup[x], tin[y]);
}
else
{
int f = dfs(y, x);
fup[x] = min(fup[x], f);
if(f > tin[x])
bridges.push_back(make_pair(x, y));
else
link(x, y);
}
}
tout[x] = T++;
return fup[x];
}
void build()
{
for(auto z : bridges)
{
int x = get(z.first);
int y = get(z.second);
st = x;
t[x].push_back(y);
t[y].push_back(x);
}
}
pair<int, int> bfs(int x)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
d[i] = n + 1;
d[x] = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
int last = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
last = q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto y : t[last])
if(d[y] > d[last] + 1)
{
d[y] = d[last] + 1;
q.push(y);
}
}
return make_pair(last, d[last]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
rnk[i] = 1, p[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
--x;
--y;
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(0);
build();
pair<int, int> p1 = bfs(st);
pair<int, int> p2 = bfs(p1.first);
printf("%d\n", p2.second);
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение с персистентным ДО
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = int(1e9);
const int N = 500001;
typedef pair<int, int> pt;
#define x first
#define y second
#define mp make_pair
struct node
{
pt val;
node* l;
node* r;
node() : val(mp(INF, 0)), l(NULL), r(NULL) {};
node(node* l, node* r)
{
this->val = min(l->val, r->val);
this->l = l;
this->r = r;
}
node(int pos, int val)
{
this->val = mp(val, pos);
this->l = NULL;
this->r = NULL;
}
};
typedef node* stree;
pt query(stree t, int l, int r, int L, int R)
{
if(L >= R)
return mp(INF, 0);
if(l == L && r == R)
return t->val;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
pt q1 = query(t->l, l, mid, L, min(mid, R));
pt q2 = query(t->r, mid, r, max(mid, L), R);
return min(q1, q2);
}
stree update(stree t, int l, int r, int pos, int val)
{
if(l == r - 1)
return new node(pos, val);
else
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(pos < mid)
return new node(update(t->l, l, mid, pos, val), t->r);
else
return new node(t->l, update(t->r, mid, r, pos, val));
}
}
stree build(int l, int r)
{
if(l == r - 1)
return new node(l, INF);
else
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return new node(build(l, mid), build(mid, r));
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector<int> a(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
vector<int> left(n);
map<int, int> last;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(!last.count(a[i]))
left[i] = -1;
else
left[i] = last[a[i]];
last[a[i]] = i;
}
vector<stree> T(n + 1);
T[0] = build(0, n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
stree cur = T[i];
if(left[i] != -1)
cur = update(cur, 0, n, left[i], INF);
cur = update(cur, 0, n, i, left[i]);
T[i + 1] = cur;
}
int q;
scanf("%d", &q);
for(int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
int l, r;
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
--l;
pt ans = query(T[r], 0, n, l, r);
if(ans.x < l)
printf("%d\n", a[ans.y]);
else
printf("0\n");
}
}
Решение с персистентным ДО (менее читаемое, но более быстрое)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = int(1e9);
const int N = 500001;
typedef pair<int, int> pt;
#define x first
#define y second
#define mp make_pair
const int M = 60 * N;
pt bufp[M];
int lf[M];
int rg[M];
int szt = 0;
int newnode(pt val)
{
bufp[szt] = val;
return szt++;
}
int newnode(int l, int r)
{
lf[szt] = l;
rg[szt] = r;
if(bufp[l].x < bufp[r].x)
bufp[szt] = bufp[l];
else
bufp[szt] = bufp[r];
return szt++;
}
pt curans;
void query(int t, int l, int r, int L, int R)
{
if(L >= R)
return;
if(l == L && r == R)
{
if(bufp[t].x < curans.x)
curans = bufp[t];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
query(lf[t], l, mid, L, min(mid, R));
query(rg[t], mid, r, max(mid, L), R);
}
int update(int t, int l, int r, int pos, int val)
{
if(l == r - 1)
return newnode(mp(val, pos));
else
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(pos < mid)
return newnode(update(lf[t], l, mid, pos, val), rg[t]);
else
return newnode(lf[t], update(rg[t], mid, r, pos, val));
}
}
int build(int l, int r)
{
if(l == r - 1)
return newnode(mp(INF, l));
else
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return newnode(build(l, mid), build(mid, r));
}
}
int last[N];
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector<int> a(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
vector<int> left(n);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
last[i] = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
left[i] = last[a[i]];
last[a[i]] = i;
}
vector<int> T(n + 1);
T[0] = build(0, n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int cur = T[i];
if(left[i] != -1)
cur = update(cur, 0, n, left[i], INF);
cur = update(cur, 0, n, i, left[i]);
T[i + 1] = cur;
}
int q;
scanf("%d", &q);
for(int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
int l, r;
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
--l;
curans = mp(INF, 0);
query(T[r], 0, n, l, r);
if(curans.x < l)
printf("%d\n", a[curans.y]);
else
printf("0\n");
}
}
Решение с обычным ДО
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define forn(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < int(n); i++)
#define x first
#define y second
const int N = 500 * 1000 + 13;
const int INF = 1e9;
pair<pair<int, int>, int> t[4 * N];
void build(int v, int l, int r){
if (l == r - 1){
t[v] = make_pair(make_pair(INF, INF), l);
return;
}
int m = (l + r) / 2;
build(v * 2, l, m);
build(v * 2 + 1, m, r);
t[v] = min(t[v * 2], t[v * 2 + 1]);
}
void update(int v, int l, int r, int pos, int prv, int nxt){
if (l == r - 1){
t[v].x = make_pair(nxt, prv);
return;
}
int m = (l + r) / 2;
if (pos < m)
update(v * 2, l, m, pos, prv, nxt);
else
update(v * 2 + 1, m, r, pos, prv, nxt);
t[v] = min(t[v * 2], t[v * 2 + 1]);
}
pair<pair<int, int>, int> get(int v, int l, int r, int L, int R){
if (L >= R)
return make_pair(make_pair(INF, INF), -1);
if (l == L && r == R)
return t[v];
int m = (l + r) / 2;
return min(get(v * 2, l, m, L, min(m, R)), get(v * 2 + 1, m, r, max(m, L), R));
}
int n, m;
int a[N];
pair<pair<int, int>, int> q[N];
int pos[N];
int ans[N];
bool comp(const pair<pair<int, int>, int> &a, const pair<pair<int, int>, int> &b){
return a.x.y < b.x.y;
}
int main() {
memset(pos, -1, sizeof(pos));
scanf("%d", &n);
forn(i, n) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &m);
forn(i, m){
scanf("%d%d", &q[i].x.x, &q[i].x.y);
--q[i].x.x, --q[i].x.y;
q[i].y = i;
}
sort(q, q + m, comp);
build(1, 0, n);
int lst = -1;
forn(i, m){
int l = q[i].x.x;
int r = q[i].x.y;
for (int j = lst + 1; j <= r; ++j){
if (pos[a[j]] != -1)
update(1, 0, n, pos[a[j]], -INF, j);
update(1, 0, n, j, pos[a[j]], -INF);
pos[a[j]] = j;
}
auto it = get(1, 0, n, l, r + 1);
if (it.y == -1 || it.x.x != -INF || it.x.y >= l){
ans[q[i].y] = 0;
}
else{
ans[q[i].y] = a[it.y];
}
lst = r;
}
forn(i, m)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
Решение с алгоритмом Мо
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define forn(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < int(n); i++)
#define x first
#define y second
const int N = 500 * 1000 + 13;
const int P = 800;
const int INF = 1e9;
bool comp(const pair<pair<int, int>, int> &a, const pair<pair<int, int>, int> &b){
int num = a.x.x / P;
if (num != b.x.x / P)
return a.x.x < b.x.x;
if (num & 1)
return a.x.y < b.x.y;
return a.x.y > b.x.y;
}
int val[N];
int cnt[N];
int bl[P];
int tot;
inline void add(int x){
++cnt[x];
if (cnt[x] == 1){
++val[x];
++bl[x / P];
++tot;
}
else if (cnt[x] == 2){
--val[x];
--bl[x / P];
--tot;
}
}
inline void sub(int x){
--cnt[x];
if (cnt[x] == 1){
++val[x];
++bl[x / P];
++tot;
}
else if (cnt[x] == 0){
--val[x];
--bl[x / P];
--tot;
}
}
int get(){
if (tot == 0)
return 0;
forn(i, P){
if (bl[i] > 0){
for (int j = i * P;; ++j){
if (val[j]){
return j;
}
}
}
}
assert(false);
}
int n, m;
int a[N], ans[N];
pair<pair<int, int>, int> q[N];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
forn(i, n) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &m);
forn(i, m){
scanf("%d%d", &q[i].x.x, &q[i].x.y);
--q[i].x.x, --q[i].x.y;
q[i].y = i;
}
sort(q, q + m, comp);
int l = 0, r = -1;
forn(i, m){
int L = q[i].x.x;
int R = q[i].x.y;
while (r < R){
++r;
add(a[r]);
}
while (r > R){
sub(a[r]);
--r;
}
while (l > L){
--l;
add(a[l]);
}
while (l < L){
sub(a[l]);
++l;
}
ans[q[i].y] = get();
}
forn(i, m)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fore(i, l, r) for(int i = int(l); i < int(r); i++)
#define sz(a) int((a).size())
#define all(a) (a).begin(), (a).end()
#define x first
#define y second
typedef long long li;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pt;
template<class A, class B> ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, const pair<A, B> &p) {
return out << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y << ")";
}
template<class A> ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, const vector<A> &v) {
out << "[";
fore(i, 0, sz(v)) {
if(i) out << ", ";
out << v[i];
}
return out << "]";
}
const int M = 400 * 1000 + 555;
const int N = 300 * 1000 + 555;
const int LOGN = 19;
int n, m, a[N];
vector<pt> g[N];
inline bool read() {
if(!(cin >> n >> m))
return false;
fore(i, 0, n)
assert(scanf("%d", &a[i]) == 1);
fore(i, 0, n - 1) {
int u, v, w;
assert(scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w) == 3);
u--, v--;
g[u].emplace_back(v, w);
g[v].emplace_back(u, w);
}
fore(i, 0, n)
sort(all(g[i]));
return true;
}
int tin[N], tout[N], T = 0;
int p[N][LOGN];
int h[N];
li d1[N];
void calc1(int v, int pr) {
tin[v] = T++;
p[v][0] = pr;
fore(st, 1, LOGN)
p[v][st] = p[p[v][st - 1]][st - 1];
d1[v] = a[v];
fore(i, 0, sz(g[v])) {
int to = g[v][i].x;
int w = g[v][i].y;
if(to == pr)
continue;
h[to] = h[v] + 1;
calc1(to, v);
d1[v] += max(0ll, d1[to] - 2ll * w);
}
tout[v] = T++;
}
li dp[N];
vector<li> dto[N];
void calcRRT(int v) {
dp[v] = a[v];
dto[v].assign(sz(g[v]), 0ll);
fore(i, 0, sz(g[v])) {
int to = g[v][i].x;
int w = g[v][i].y;
li curVal = max(0ll, d1[to] - 2ll * w);
dp[v] += curVal;
dto[v][i] = curVal;
}
fore(i, 0, sz(g[v])) {
int to = g[v][i].x;
if(h[to] < h[v])
continue;
li tmp = d1[v];
d1[v] = dp[v] - dto[v][i];
calcRRT(to);
d1[v] = tmp;
}
}
inline bool isP(int l, int v) {
return tin[l] <= tin[v] && tout[v] <= tout[l];
}
int lca(int u, int v) {
if(isP(u, v)) return u;
if(isP(v, u)) return v;
for(int st = LOGN - 1; st >= 0; st--)
if(!isP(p[v][st], u))
v = p[v][st];
return p[v][0];
}
li getDto(int v, int to) {
int pos = int(lower_bound(all(g[v]), pt(to, -1)) - g[v].begin());
if(pos >= sz(g[v]) || g[v][pos].x != to)
return 0;
return dto[v][pos];
}
li f[N];
inline void inc(int pos, li val) {
for(; pos < N; pos |= pos + 1)
f[pos] += val;
}
inline li sum(int pos) {
li ans = 0;
for(; pos >= 0; pos = (pos & (pos + 1)) - 1)
ans += f[pos];
return ans;
}
inline li getSum(int l, int r) {
return sum(r) - sum(l);
}
li ans[M];
vector<pt> qs[N];
void calcAns(int v) {
li vAdd = dp[v] - getDto(v, p[v][0]);
inc(h[v], vAdd);
for(pt &q : qs[v]) {
int up = q.x, id = q.y;
ans[id] += getSum(h[up] - 1, h[v]) + getDto(up, p[up][0]);
}
fore(i, 0, sz(g[v])) {
int to = g[v][i].x;
int w = g[v][i].y;
if(h[to] < h[v])
continue;
li curSub = dto[v][i] + w;
inc(h[v], -curSub);
calcAns(to);
inc(h[v], +curSub);
}
inc(h[v], -vAdd);
}
inline void solve() {
T = 0;
h[0] = 0;
calc1(0, 0);
calcRRT(0);
fore(i, 0, m) {
int u, v;
assert(scanf("%d%d", &u, &v) == 2);
u--, v--;
int l = lca(u, v);
ans[i] = -dp[l];
qs[u].emplace_back(l, i);
qs[v].emplace_back(l, i);
}
calcAns(0);
fore(i, 0, m)
printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
}
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
int tt = clock();
#endif
cout << fixed << setprecision(15);
if(read()) {
solve();
#ifdef _DEBUG
cerr << "TIME = " << clock() - tt << endl;
tt = clock();
#endif
}
return 0;
}









Can F be solved with a mergesort tree? ( By keeping all the elements which occur once in the nodes, where each node is a sorted vector. Also, merging is easy. )
How is merging easy? Sounds like at least O(n) if it's two pointers. Let the array be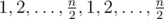 and all the queries are [1, n - 1]. How can you merge nodes fast enough?
and all the queries are [1, n - 1]. How can you merge nodes fast enough?
Damn, sorry.
I used merge sort tree keeping for each element the range in which it's not repeated : My submission
I used merge sort tree and passed with a time of $$$2901 \text{ ms}$$$, maybe should've used other method instead :/
submission: Accepted
I like the fact that you have given different approaches for solving F. Thanks.
In B that's enough to check a_i + 1 only
You don't right.
Why not?
hmm
Am I wrong in the situaton when there are two adjacent points?
I didn't think about it because my solution had AC
Could you give a case please. Because if there are only 2 points the solution would be put nothing
No, I meant another thing. It's correct that making a point in a_i-1 and a_i+1 would give the same result. But sometimes it's impossible to put a point in a_i+1(like if there are points with coordinates x and x+1)
There are some facts I can't prove because of my bad Englsh)) They are not very hard, but I can try to write proofs for them in Russian if you would want)
It's enough. If we can put a point in ai + 1 and ai - 1, the result will be the same. So I can be wrong in a situation when we can put a point in ai - 1 but can't in ai + 1. Let's take a look at this. The points must be like ...ai - 1, ai, ai + 1(because we can't make a point at here)... Let's increase i until we find a free ai + 1. What do we get? A sequence of adjacent points. I want to say that the result will be the same if we put a point in the left of this sequence or in the right.
If we don't find this i, it means there is a sequence with the end at M. in that case I say that the result will be the same if we put a point in the left or don't put at all.
А это нормально, что у меня tl на 9 тесте, когда я отправляю авторское решение с МО?
Нормально, у меня в полигоне оно тоже ТЛ ловит, надо его оптимизировать еще.
нет
Mo-based solution for problem 1000F - One Occurrence is getting TLE
At first I try to write a solution with help of Mo-based solution Editorial, but I getting TLE, after getting many TLE I submit the code from Editorial exactly, but this also getting TLE...:(
We never said Mo-based solution from the editorial gets AC. You still need to optimize things here and there.
See my submission using Mo's approach 39747523
At last I get AC with a lot of change, but using Mo's approach. Here it is 39751860
i have a question with Mo's algorithm
why use this cmp could get AC
other cmp will get TLE
See this comment
I learned this trick from meooow. You can check it out here : Link.
Accepted with other cmp
Can anyone explain normal segment tree approach for 1000F - One Occurrence ?
Link
What will happen in E if the graph is complete graph? there will not be any bridge. so what will be the answer?
What will happen in E if the graph is complete graph? there won't be any bridge. so what will be the answer?
0
Ok. Thanks. I read the announcement and finally understood question well.
The problem F is very similar to this problem from BZOJ.
Sorry for my poor English.
But foreigners don't know BZOJ:(
Nor can they read Chinese:(
Can anyone elaborate 1000D.
dp[i] is the number of good sequences on the suffix from the i-th element. and dp[n + 1] = 1
and dp[n + 1] = 1
Then
please explain that logic with an appropriate example ...it'll be a great help :)
why are we multiplying with dp[j+1] int the above formula.
We can choose sequense of length a[i] whith start from i and finish to j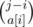 ways. After it you solve this problem on the suffix from j + 1 for other way of binom.
ways. After it you solve this problem on the suffix from j + 1 for other way of binom.
thanks :)
Mo-based solution of Problem F doesn't get AC.
Thanks for information! It is being discussed 3 comments higher.
Is it possible to use F's solution to query element that occurs exactly t times on a segment?
I think that in this case we would go with persistent ST from right to left (instead of left->right as in editorial). Suppose we are making a version that corresponds to l'th element of an array. We could precompute indices of occurrence of every array element. Suppose array[l] has more or equal than t - 1 occurrences after l: in this case we should update index of t - 1'th position with an index of t'th one or ∞ if such doesn't exist. So, the version l now contains t + 1'th occurrences of t'th elements. Initial version is initialized with negative infinities.
Now, the query [l, r] is the range maximum query [l, r] on l'th version.
As in editorial one needs to unset t + 1'th position assigning negative infinity to it.
I also realized that we could build the tree from left to right and do range minimum queries just as in editorial.
Please, tell me if there is an apparent flaw in this solution.
Anyone please explain the solution of Problem 1000F with standard segment tree
Why do we need to 'keep only the unique values' in the solution for problem C? I got AC with this and it was pretty straightforward.
what is the use of "mark" in your code?
My bad, that part is redundant, it was for marking the pevents for the small coordinates case. Ignore it here.
Ok.
I got it :) sorry for that comment
We can solve G online with same approach from editorial. Let f(2^i, u) is maximal profit of 2-path from u to 2^i th ancestor of u. f can easily calculated using d' and dp in editorial. Then, we can solve query (u, v) by binary jump on tree (similar to finding LCA).
Code: 39743132
Слишком сложное объяснение С, как по мне, есть намного более легкий способ. Разве что автор объяснил, что есть "Метод сжатия координат".
Мое решение , основанное на разделении на подотрезки:
http://codeforces.com/contest/1000/submission/39776916
int tp = (i & 1) ^ 1; meaning in B solution code??Can anyone explain
tp is 1 if i is even and is 0 otherwise
Can anyone suggest a good resource for understanding and implementing bridges in a graph ?
this might help -> https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/graphs/articulation-points-and-bridges/tutorial/ and https://threads-iiith.quora.com/The-Bridge-Tree-of-a-graph
Is this some kind of hashing of edges?
y = A[h] ^ B[h] ^ x;in Farhod's solution for 1000G.There's another way to do problem D that might make the code simplier. Maintain a dp[][] where the first dimension is the index you are at and the second dimension is the number of integers you have to choose to include before you can open another good sequence.
dp[i][k] is simply the sum of:
At the beginning, dp[0][0] = 1. At the end, the answer is dp[n][0] — 1 (because empty subsequence isn't allowed)
This is the code:
http://codeforces.com/contest/1000/submission/39787639
Opps and forget my dfs function it's not part of the solution.
My solution for Problem B — Light it up
https://coolforces.blogspot.com/2018/06/1000b-codeforces-light-it-up-solution.html
We don't necessarily have to answer the queries offline in 1000G.
Another cool dp for G: You can use the dp i -> i, and another one called "dpBestToRoot" which saves the best path to root (which is basically the best detour downward + the bestPathToRoot of your parent + the weight between you and your parent — your part in the detour of your parent).
Now you just do dpBestToRoot[u]+dpBestToRoot[v]-2*dpBestToRoot[lca]+dp[lca]. (http://codeforces.com/contest/1000/submission/39811424)
I think more straightforward solution for G is to count dpv than build heavy light decomposition with prefix sums of ways where value for each node would be dpv - ev, u - max(dpu - 2 * ev, u) where v is node and u is child of v that lying on the same way(you know this ways in HLD) 39742958
In fact, problem C can be solved with O(n) complexity,I think :P
Sorry,my fault,sorting costs O(nlogn) too :P
В задаче F для того чтобы алгоритм МО заходил совсем не обязательно хранить sqrt декомпозицию. Сделаем такую вещь. Создадим стек и массив пометок, где для каждого числа от 1 до maxa будет записано есть ли оно в стеке. Теперь, когда на надо добавить число, мы добавляем его если его еще нет в стеке (для этого нужен массив пометок), если нужно удалить элемент ничего не делаем. Теперь заметим, что в каждый момент времени в стеке лежат элементы, которые могут быть потенциальным ответом. Теперь, чтобы получить ответ, мы удаляем верхний элемент из стека (не забывая снять пометку) пока он не ответ. Заметим, что суммарно движений границы порядка nsqrt(n), значит суммарно таких добавлений/удаления nsqrt(n), что не портит ассимптотику, добавляет это O(n) памяти, что не критично. Моя посылка с этом решением на раунде
https://codeforces.com/contest/1000/submission/39713669
Anyone Plz HELP me for 1000C — Covered Points Count I am implementing the same logic as describes above but getting WA for Test Case 4 For Points Covered by 1 Segment. My Code — 39936831 THANKS IN ADVANCE
In G, since wi > 0, does it matter if we remove the "twice" constraint in the statement?
This block is superb.
In problem E, what is being asked in the question and why the answer for that is equal to the diameter of the bridge tree instead of the total number of bridges?
I also did not understand at the beginning. In the problem they ask to find two vertex such that the number of bridges between them is maximum The task does not give specific starting and finishing positions, you need to find such that the number of bridges between them is maximum (shortest path)
Understood. Thanks for the help
For problem F, I used a mergesort tree to get online queries in $$$O(\log^2 n)$$$ (barely snuck under the time limit).
Let each element in the array be a triple $$$(l, r, x)$$$, where $$$x$$$ is the value of that element, $$$l$$$ is the index of the previous occurrence of value $$$x$$$ in the array $$$+1$$$, and $$$r$$$ is the index of the next occurrence of value $$$x$$$ in the array $$$-1$$$. If there is no next or previous occurrence, then just use $$$+\infty$$$ or $$$-\infty$$$ or something.
Now, to query an interval $$$[a, b]$$$, we would like to know if there exists any triple $$$(l, r, x)$$$ in the array between indices $$$a$$$ and $$$b$$$, such that $$$l\leq a$$$ and $$$r\geq b$$$. If any such triple exists, we return $$$x$$$.
Now, we build a mergesort tree on the triples $$$(l, r, x)$$$ (sorted by $$$l$$$). Each node of the segment tree will store a sorted list of the triples on some interval, as well as a list of pairs $$$(r, x)$$$ which denote prefix maximums in terms of $$$r$$$ (and $$$x$$$ just gets copied over from whichever element had the largest $$$r$$$), on that sorted list.
Next, using normal segment tree tactics, we can make it so that for a query interval $$$[a, b]$$$, we only need to examine $$$O(\log n)$$$ nodes to try and find some valid $$$x$$$. For each node, we binary search the sorted list of triples to get a prefix such that $$$l\leq a$$$, and then take the corresponding $$$(r, x)$$$ at the end of that prefix, which gives us the largest possible $$$r$$$ on that prefix. If $$$r<b$$$, then no valid solution exists, otherwise the $$$x$$$ that we found is valid. Examining one node thus takes $$$O(\log n)$$$ time.
So, we can query an interval $$$[a, b]$$$ in $$$O(\log^2 n)$$$ time. Submission here: 84532864
strict time limit for problem F even edutorial solutions get TLE
To find the answer for each query, we can do a query on the segment tree, let's call it $$$FIND(l,r)$$$ operation, for the time being...
Basic idea: Sort queries with endpoints, index segtree with last occurrence index, and find if any value's prev last occurrence is in out of range.
Code : https://codeforces.com/contest/1000/submission/214379121
Complexity: $$$O(NlogN)$$$
Problem G can be solved online in same complexity of $$$O((n + q)\log{n})$$$ with any tree path sum structure and some additional precomputation.
Implementation: link
can anybody explain what problem E is asking ?