Pasha is a good student and one of MoJaK's best friends. He always have a problem to think about. Today they had a talk about the following problem.
We have a forest (acyclic undirected graph) with n vertices and m edges. There are q queries we should answer. In each query two vertices v and u are given. Let V be the set of vertices in the connected component of the graph that contains v, and U be the set of vertices in the connected component of the graph that contains u. Let's add an edge between some vertex 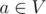 and some vertex in
and some vertex in 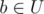 and compute the value d of the resulting component. If the resulting component is a tree, the value d is the diameter of the component, and it is equal to -1 otherwise. What is the expected value of d, if we choose vertices a and b from the sets uniformly at random?
and compute the value d of the resulting component. If the resulting component is a tree, the value d is the diameter of the component, and it is equal to -1 otherwise. What is the expected value of d, if we choose vertices a and b from the sets uniformly at random?
Can you help Pasha to solve this problem?
The diameter of the component is the maximum distance among some pair of vertices in the component. The distance between two vertices is the minimum number of edges on some path between the two vertices.
Note that queries don't add edges to the initial forest.
The first line contains three integers n, m and q(1 ≤ n, m, q ≤ 105) — the number of vertices, the number of edges in the graph and the number of queries.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n), that means there is an edge between vertices ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the given graph is a forest.
Each of the next q lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n) — the vertices given in the i-th query.
For each query print the expected value of d as described in the problem statement.
Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6. Let's assume that your answer is a, and the jury's answer is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 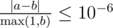 .
.
3 1 2
1 3
3 1
2 3
-1
2.0000000000
5 2 3
2 4
4 3
4 2
4 1
2 5
-1
2.6666666667
2.6666666667
In the first example the vertices 1 and 3 are in the same component, so the answer for the first query is -1. For the second query there are two options to add the edge: one option is to add the edge 1 - 2, the other one is 2 - 3. In both ways the resulting diameter is 2, so the answer is 2.
In the second example the answer for the first query is obviously -1. The answer for the second query is the average of three cases: for added edges 1 - 2 or 1 - 3 the diameter is 3, and for added edge 1 - 4 the diameter is 2. Thus, the answer is 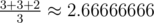 .
.