You are given a directed graph, consisting of n vertices and m edges. The vertices s and t are marked as source and sink correspondingly. Additionally, there are no edges ending at s and there are no edges beginning in t.
The graph was constructed in a following way: initially each edge had capacity ci > 0. A maximum flow with source at s and sink at t was constructed in this flow network. Let's denote fi as the value of flow passing through edge with index i. Next, all capacities ci and flow value fi were erased. Instead, indicators gi were written on edges — if flow value passing through edge i was positive, i.e. 1 if fi > 0 and 0 otherwise.
Using the graph and values gi, find out what is the minimum possible number of edges in the initial flow network that could be saturated (the passing flow is equal to capacity, i.e. fi = ci). Also construct the corresponding flow network with maximum flow in it.
A flow in directed graph is described by flow values fi on each of the edges so that the following conditions are satisfied:
A flow is maximum if the difference between the sum of flow values on edges from the source, and the sum of flow values on edges to the source (there are no such in this problem), is maximum possible.
The first line of input data contains four positive integers n, m, s, t (2 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ m ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ s, t ≤ n, s ≠ t) — the number of vertices, the number of edges, index of source vertex and index of sink vertex correspondingly.
Each of next m lines of input data contain non-negative integers ui, vi, gi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, 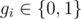 ) — the beginning of edge i, the end of edge i and indicator, which equals to 1 if flow value passing through edge i was positive and 0 if not.
) — the beginning of edge i, the end of edge i and indicator, which equals to 1 if flow value passing through edge i was positive and 0 if not.
It's guaranteed that no edge connects vertex with itself. Also it's guaranteed that there are no more than one edge between each ordered pair of vertices and that there exists at least one network flow that satisfies all the constrains from input data.
In the first line print single non-negative integer k — minimum number of edges, which should be saturated in maximum flow.
In each of next m lines print two integers fi, ci (1 ≤ ci ≤ 109, 0 ≤ fi ≤ ci) — the flow value passing through edge i and capacity of edge i.
This data should form a correct maximum flow in flow network. Also there must be exactly k edges with statement fi = ci satisfied. Also statement fi > 0 must be true if and only if gi = 1.
If there are several possible answers, print any of them.
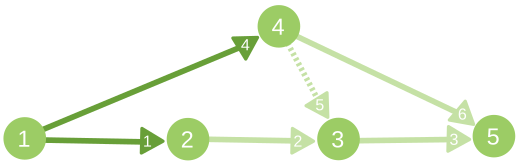
5 6 1 5
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 5 1
1 4 1
4 3 0
4 5 1
2
3 3
3 8
3 4
4 4
0 5
4 9
The illustration for second sample case. The saturated edges are marked dark, while edges with gi = 0 are marked with dotted line. The integer on edge is the index of this edge in input list.