Решение: 7407613;
В этой задаче надо было проверить существования таких i и j, что i ≠ j, a[i] < a[j], b[i] > b[j]. Если существуют такие i и j, то Леша рад.
Для этой задачи есть очень простое решение. Просто проверить, что для всех i верно, что a[i] = b[i]. Если это так, то Леша не рад.
Доказательство очень простое. Давайте отсортируем массивы a и b, как пары чисел, по возрастанию. Можно увидеть что Лёша рад, если есть хотя бы одна инверсия в массиве b, то есть существуют такие i и j, что b[i] > b[j] и i < j (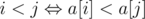 , так как числа в массиве a идут в возрастающем порядке). То есть это значит, что массив b не отсортирован, и это значит, что a ≠ b.
, так как числа в массиве a идут в возрастающем порядке). То есть это значит, что массив b не отсортирован, и это значит, что a ≠ b.
В этой задаче надо было вычислить то, что просили в условии. Правда в лоб это не легко сделать.
Но если посмотреть на формулу, то можно сделать следующее:
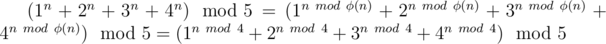
Эта формула верна, потому что 5 — простое число и оно взаимнопросто с 1, 2, 3, 4.
Чтобы применить это решение, нужно уметь брать остаток от деления на 4 длинного числа и уметь вычислять выражение для маленького n.
Асимптотика — 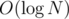 .
.
Можно было писать другое решение. Более лобовое. Можно было использовать быстрое возведение в степень, но не бинарное. Идея та же, что и у бинарного возведения. Пусть мы возводим число x в степень n по модулю P. Мы должны двигаться по длинному числу n с конца и хранить два значения: Result — текущий результат и K — число x возведенное в 10i, где i — номер разряда на котором мы стоим (разряды нумеруются с конца начиная с нуля). Чтобы обновить ответ надо сделать следующее: 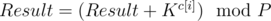 , c[i] — i-ая цифра числа n с конца.
, c[i] — i-ая цифра числа n с конца.
Асимптотика — 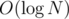 .
.
В этой задаче вам надо было максимизировать сумму набранных очков. Давайте подсчитаем количество всех чисел в массиве a, то есть заведем массив cnt, где cnt[x] — количество чисел x в массиве a. Теперь очень просто считать ДП. Оно имеет такой вид:
f(i) = max(f(i - 1), f(i - 2) + cnt[i]·i), 2 ≤ i ≤ n;
f(1) = cnt[1];
f(0) = 0;
Ответ будет содержаться в f(n).
Асимптотика — O(n).
456D - Много игр / 455B - Много игр
Давайте научимся определять, может ли игрок выиграть и может ли проиграть в одной игре. Для этого нам понадобится префиксное дерево(бор), сформированние из всех строк набора. Будем считать два ДП — win[v], lose[v]. Если v — лист бора, то win[v] = false;lose[v] = true.
Иначе win[v] = (win[v] or (not win[i])); lose[v] = (lose[v] or (not lose[i])), по всем i — детям вершины v.
Теперь осталось рассмотреть пару случаев:
Если win[v] = false, то выигрывает второй игрок (то есть первый игрок будет все k игр проигрывать и начинать заново новую игру, так как он проиграл в прошлой игре).
Если win[v] = true и lose[v] = true, то выигрывает первый игрок (тут первый игрок может в первой игре изменить ход событий в свою пользу).
Иначе у нас остается только один случай — win[v] = true и lose[v] = false, то тут исход игры зависит от четности k, если k mod 2 = 1, то выигрывает первый игрок, иначе второй (в этом случае игроки будут по очереди выигрывать и всё зависит от чётности k).
Асимптотика — 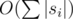 .
.
456E - Цивилизация / 455C - Цивилизация
Во-первых можно было заметить, что наша система дорог всегда будет оставаться лесом деревьев. Для эффективного хранения компонент следует использовать СНМ (система непересекающихся множеств). Вначале нужно построить начальную систему дорог. В каждой компоненте начальной системы дорог нужно найти диаметр компоненты. Это можно сделать обходом в ширину или глубину. Пусть a — произвольная вершина. Тогда b — самая далекая вершина от вершины a. И c — самая далекая вершина от вершины b. Расстояние от вершины b до вершины c — диаметр. Все эти утверждения верны только для дерева. Теперь для каждого множества в СНМ мы знаем его диаметр. Теперь очень легко отвечать на запрос первого типа: Узнать в каком множестве лежит вершина x и вывести диаметр этого множества. Запрос второго типа тоже легко обработать: Пусть u — номер множества в котором лежит вершина x, v — номер множества в котором лежит вершина y. Теперь если u ≠ v, то можно объеденять эти два множества в новое множество. Диаметр нового множетсва вычисляется так:
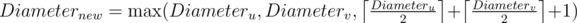
Асимптотика — O(n·A - 1(n)), где A - 1(n) — обратная функция Аккермана.
Решения: 7407693, 7407699, 7407703;
Давайте сведем запрос 1-го типа к двум более простым более простым запросам:
Удалить число из массива на r-ой позиции. Вставить это же число в массив на l-ую позицию, то есть после (l - 1)-ой позиции.
Теперь давайте хранить наш массив, как 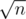 блоков. В каждом блоке будем хранить сами числа в таком порядке, как в массиве a и будем хранить массив cnt. cnt[x] — количество чисел x в блоке. Всё это будет требовать
блоков. В каждом блоке будем хранить сами числа в таком порядке, как в массиве a и будем хранить массив cnt. cnt[x] — количество чисел x в блоке. Всё это будет требовать 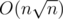 памяти.
памяти.
Теперь легко быстро выполнять запрос 1-го типа. Удалить число с r-ой позиции мы можем за 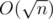 операций. А потом уже вставить это же число тоже можем за
операций. А потом уже вставить это же число тоже можем за 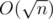 операций. За O(1) мы так же можем обновлять массив cnt. Асимптотика выполнения первого запроса —
операций. За O(1) мы так же можем обновлять массив cnt. Асимптотика выполнения первого запроса — 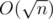 .
.
Так же легко быстро выполнять запрос 2-го типа. Нужно пройтись всего по 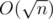 блокам, которые полностью попадают под границы запроса. И нужно пройтись по
блокам, которые полностью попадают под границы запроса. И нужно пройтись по 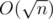 числам, которые лежат в блоках, которые частично попали в запрос.
числам, которые лежат в блоках, которые частично попали в запрос.
Чтобы сохранять размеры блоков близкими к 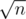 , нужно каждые
, нужно каждые 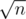 запросов 1-го вида перестраивать наши блоки. Перестройка делается за O(n).
запросов 1-го вида перестраивать наши блоки. Перестройка делается за O(n).
Итоговая асимптотика — 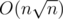 .
.
В этой задаче нужно было быстро уметь считать описанную в условии функцию.
Можно свести задачу нахождения значения функции f(x, y) к более простой задаче:
Пройти по массиву a, начиная от позиции y, сделав (x - 1) шаг. Шаг может быть таким: либо пойти влево, либо остаться на месте.
Значение функции 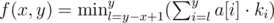 , где ki — сколько раз мы посетили i-ый элемент массива a.
, где ki — сколько раз мы посетили i-ый элемент массива a.
Для фиксированного l понятно, выгоднее всего, чтобы минимум на отрезке [l, y] был посещен (x - (y - l)) раз, а все остальные числа по одному разу. Ещё можно заметить, что нам выгодно, чтобы a[l] был минимумом.
Из всего этого можно сделать вывод, что для фиксированного l ответом будет — sum[y] - sum[l] + a[l]·(x - (y - l)), где sum — массив префиксных сумм массива a.
Формулу выше можно расписать так:
sum[y] - sum[l] + a[l]·(x - (y - l)) = sum[y] - sum[l] + a[l]·(x - y + l) = sum[y] - sum[l] + a[l]·l + a[l]·(x - y) = sum[y] + (a[l]·(x - y) + a[l]·l - sum[l])
Можно заметить, что в скобках вышло что-то похожее на уравнение прямой — K·X + B. В скобках вышло: a[l]·(x - y) + a[l]·l - sum[l], где K = a[l], X = (x - y), B = a[l]·l - sum[l].
Теперь нам осталось научиться для всех подходящих l научиться искать минимум на всех прямых при фиксированном X = (x - y).
Прямых у нас будет n. То есть для каждого элемента массива a своя прямая. Теперь ответ на запрос будет равен:
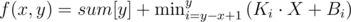 , где (Ki, Bi) — i-ая прямая. Ki = a[i], Bi = a[i]·i - sum[i].
, где (Ki, Bi) — i-ая прямая. Ki = a[i], Bi = a[i]·i - sum[i].
Чтобы вычислять ответ на запрос быстрее, чем простой проход по прямым, нужно ипользовать Convex Hull Trick на дереве отрезков. То есть в каждой вершине дерева отрезков мы храним все прямые, за которые отвечает эта вершина. Итого у нас будет израсходовано 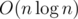 памяти. А запрос будет выполняться за
памяти. А запрос будет выполняться за 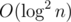 операций. Так как мы посетим
операций. Так как мы посетим 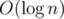 вершин и в каждой вершине выполним
вершин и в каждой вершине выполним 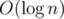 операций. Подробнее познакомиться с Convex Hull Trick вы можете тут.
операций. Подробнее познакомиться с Convex Hull Trick вы можете тут.
Асимптотика — 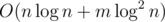 .
.




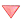





Длинная арифметика здесь даже не нужна. Для всякого числа n
где b — последние две цифры n. Поэтому достаточно просто взять остаток от деления последних двух цифр на 4.
А можно добавить авторские решения?
Добавил
Как в задаче Д первого дивизиона узнать количество нужного числа в блоке? Единственное, что приходит на мысль-хештаблица для каждого блока, но сомневаюсь, что зайдет по ТЛ.
upd. Свою ошибку понял. Игнорируйте этот коммент. (\/)(*--*)(\/)
Более простое решение по Б. Как уже сказал andreyv, достаточно взять две последние цифры числа n, чтобы узнать, делится ли оно на 4.
Теперь нужно рассмотреть степени чисел
1, 2, 3, 4:1 1 1 1 ...2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 ...3 9 27 81 243 ...4 16 64 256 ...Можно заметить повторение последней цифры (при делении на 5 нам достаточно знать последнюю цифру каждого числа):
1:12:2 4 8 63:3 9 7 14:4 6То есть единица в любой степени будет оканчиваться на
1(да я сам капитан очевидность), два в степениn: еслиn % 4 = 1, будет оканчиваться2; еслиn % 4 = 2, будет оканчиваться4; еслиn % 4 = 3, будет оканчиваться8; и т.д.То есть достаточно сложить последние цифры степеней чисел
1, 2, 3, 4и вывести результат по модулю 5.Исходный код
P.S. Решение хоть и является сложным в рассуждениях, было написано за 10 минут. В ходе написания использовался личный опыт.
Поправка: исходный код работает неверно для теста
n = 0. В этом случае он считает не очевидное(1 + 1 + 1 + 1) % 5 = 4, а(1 + 6 + 1 + 6) % 5 = 4. Но ответ всё равно получается правильным.Стоит к контесту приложить этот разбор.
Problem D could be solve by Splay which invented by Darooha in O(nlog2n) without the ungraceful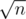 part.
part.
It is hard to answer the query if you only have one Splay. The key point is to build more splays with each different k (
k-splay). Let's call the splay with all elements0-splay.Thus, for query, you can find the interval of [l, r] on the
k-splayby a variation ofselect()function. The different of it between the regular is not use rank of the node but the rank of the corresponding node on the0-splay.For modification, you should also adjust the position of a node in
0-splayand the correspondingk-splay. So for each node, we add one more field to store the corresponding node in anothersplay.Check my submission or vfleaking's for detail.
Do u know Russian?
Why is O(nlog2n) ? I think just O(nlogn) .
Because is a implicit treap with keys linked to nodes in others implicit treaps for all k. O.o cool. code
Can you explain the logic?
sorry for forgetting this comment, today someone reminded me. The idea is not very complicated, you just have to keep a treap of all the possible values in "a", and one for each of them, rotating a range can be seen as removing the last of the range and putting it before the range, now If I only had the first query then it would be enough with the treap that has all the values, but since it is not like that, the trick is that the implicit keys of the other treaps, use the order they have in the main treap, this allows us not to have worrying about adding 1 to each value that was in the range [l, r-1], note that the structure of those treaps does not change (except the position r), this is treated separately, but it is only one that is treated differently instead of r — l + 1 positions.
Thanks bro!
really inspiring
My solution using Treap.
solution using Treap.
Any balanced tree with father pointers would work. Treap is easier to write.
Народ подскажите пожалуйста где в сети можно подробней прочитать о том трюке, который применяется в первом решении для задачи "456B — Федя и математика", i.e., что это за "φ" и почему она может применяться к показателю степени? Заранее спасибо!
Вот: Малая теорема Ферма, Теорема Эйлера
В задаче используется тот факт, что
Мне это, как-то, менее понятно. По моему проще просто заметить, что число, оканчивающееся на какую-то цифру, в целых положительных степенях будет иметь на конце определённую другую цифру. И период чередования этой последней цифры кратен четырём (для 1, 5 и 6 — период 1, для 9 и 4 — период 2). А так как при делении на 5 (или на 2, 10) нам достаточно знать только последнюю цифру, то этого будет достаточно.
e-maxx вам в помощь! :)
Исправьте разбор Div1 B. У листа lose[v]=1, а не lose[v]=0; по тому, что сейчас написано в разборе, массивы win и lose вообще ничем не отличаются.
Спасибо, исправил
Can anybody explain about How to implement the trie using an array instead of pointer??
I've used to implement tree with a 2-d array [if you guarantee 2 child for every node] the array will look like this
if you want to reach the first child of the i-th node in the j'th level :
level=j+1,id=2*ibut how we can implement trie (prefix tree) using it??
You could see my code here 7393354
Y use a trie using a vector of pairs and Grundy number to solve the game I know that my code couldn't be clear but I hope it could help you
Sorry for my english too
You do it like with the standard trie, but replace pointers with array indices and node allocation with index advance:
// Array of nodes. If trie[i].next[x] is 0, then there is no path with // character x from the node i. Otherwise it is an index of the next // node. struct trie_node { int data; int next[26]; }; trie_node trie[100005]; // Number of allocated nodes, 1 by default for trie root int count = 1; void insert(const string& s) { int p = 0; // Index of the current node, 0 by default for root for (char c : s) { int x = c - 'a'; if (trie[p].next[x] == 0) { // This is a leaf, attach new node to it. // For new node, take trie[count], and increase count. trie[p].next[x] = count++; } // Advance to the next node p = trie[p].next[x]; } trie[p].data++; }.datais the information we want to store in tree nodes. For example, it can hold the number of strings ending in this node, like it does in theinsert()function above.As an exercise write a
contains_prefix(s)function for this structure.A full structure of Trie should be a more bit representing "is some word ends here"
Good point, fixed.
in problem C div 1 when we calculate the diameter why do we maximize between diameter of the 2 trees ?
in problem C div 1 when we calculate the diameter of the new tree why do we maximize between the 2 trees ?
can some one explain "how to use the convex Hull Trick with segment Tree" in DIV-1 E
Remainder: convex hull trick lets us maintain k linear functions of the form fi(x) = aix + bi and answer efficiently (in time proportional to number of functions) to the queries Q(x) = min1 ≤ i ≤ k fi(x) (given x).
Now we will be able to solve the problem if we can answer a bit more general kind of queries: we consider only lines with indices from given L and R; formally, Q(x, L, R) = minL ≤ i ≤ R fi(x).
How can we do it? Let's make a segment tree! Let's say we have such m that 2m ≥ n. Then the root contains the convex hull of lines having indices [0, 2m - 1], its left child contains [0, 2m - 1 - 1], right child [2m - 1, 2m - 1] and so on. We can costruct all these hulls one by one; without any optimizations it gives us time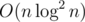 .
.
Now let's say we have to answer the query Q(x, L, R). Then we just "break" the interval [L, R] into base intervals (in the same way a segment tree does) and for each of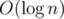 such base intervals we find its minimum at x. Now we see that the answer is the smallest of these minima. It doesn't matter that we consider some groups of lines from interval [L, R] separately — still, we can just take the smallest of the results.
such base intervals we find its minimum at x. Now we see that the answer is the smallest of these minima. It doesn't matter that we consider some groups of lines from interval [L, R] separately — still, we can just take the smallest of the results.
What's the time? We have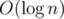 base intervals, for each of them we can compute the answer in
base intervals, for each of them we can compute the answer in 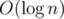 , so total time is
, so total time is 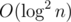 . There are some ways which let us compute all answers off-line in
. There are some ways which let us compute all answers off-line in 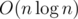 , but it's not the subject :P
, but it's not the subject :P
aix + bi -> aix + bi
@mnbvmar would you like to provide a neat and clean implimentation of convex hull Trick .It is a great help for me and naive learner's like me
http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/8219
this topic is a great way of learning about the convex hull trick. the DS itself is ~30 lines of code, really simple if you understand geometry basics
Hi. I'm new to DP. Can someone please explain me where did the formula for problem div2 C or div1 A come from? Implementing it is not hard but I have problem with the formula. Why should f[i] be as said in the editorial? I don't understand...
I would be thankful if someone could give me more explanation about it. Thanks
A more straightforward formula looks like this
Let f[i][0] = max. answer considering numbers <= i && doesn't choose i, f[i][1] = max. answer choose i
Then f[i][0] = max(f[i-1][0],f[i-1][1]), and f[i][1] = f[i-1][0] + cnt[i]*i
Actually this is doing the same thing as the formula in editorial.
I am confused as to what cnt[i] is supposed to represent. What exactly does cnt[] store?
cnt[i] is the number of the times that the number i has appeared in the input list. It can be calculated while reading the input.
cnt[i] represent the frequency of the number "i"
Shouldn't the statement be this:
Because if we don't choose
i, then we definitely have to choosei-1to removei.And if we have to choose
ithen we will have to not choosei-1=>dp[i - 1][0]and for choosing all occurrences ofiwe getcnt[i]*iAny help regarding this would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks
before doing boredom question try this one simpler version of boredom https://www.hackerearth.com/problem/algorithm/choosing-the-judges-7/description/
Thanks a lot !! It really helped me!!
Warning: please take this explanation with a pinch of salt, because I'm myself new to DP, and it may thus be incorrect ...
First, we pre-compute the frequency of occurrence of each element in Alex's sequence (using the array "freq", say)
dp[i] stores the maximum sum that Alex can get using the numbers from 1 to i. Thus, dp[0] is 0, and dp[1] is freq[1] (i.e., number of '1's in the sequence)
For i = 2 to 10^5 (10^5 being the maximum possible value of any number in Alex's sequence according to the given constraints), dp[i] is calculated using the inference that each set of "i"s (if at all they occur in the sequence) can either all be picked OR not picked at all:
dp[i] = max(I, II), where:
I = dp[i-1] represents the situation where "i" isn't picked at all (As "i" isn't picked at all, none of the "i-1"s will be deleted, and the sum will be the same as the one calculated for dp[i-1])
II = dp[i-2] + (freq[i] * i) represents the situation where all "i"s are picked (As all the "i"s are picked, all the "i-1"s WILL be deleted, and we cannot consider dp[i-1] at all, given that dp[i-1] was itself computed while considering the situation where all the "i-1"s may be picked. Instead, we use dp[i-2]; the sum computed therein is safe to use, given that none of the "i-2"s will be deleted when the "i"s are picked. Also, as we are picking all the "i"s, our previous sum (i.e., dp[i-2]) will increase by (freq[i] * i))
Final answer will just be dp[100000].
My implementation of the above logic (C++): http://codeforces.com/contest/456/submission/18021003
Thank You for the explanation!
Hello.
Could you help me?
problem C div 2.
link to task
How is it possible to get 16 from this test case?
5
5 3 5 3 4
Windboy hell_hacker RaghavN
we would choose the numbers 3 and 5. so the required sum would be : (6+10)=16.
Alternative way is to use a 2 dimensional dp.
dp[i][0] represents max value you can get from 1 to i and not picking i.
dp[i][1] represents max value from 1 to i and picking i.
The relations for each i are:
Base case- dp[0][0]=dp[0][1]=0;
dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1])'
dp[i][1]=freq[i]*i+dp[i-1][0];
Then answer would be max(dp[100000][0],dp[100000][1]).
I personally find that single dimensional dp can sometimes be tough to understand so I use 2d normally.
Implementation:21918844
Sorry for bringing up such an old thread, could you please explain why the final answer should be dp[100000] instead of dp[n] which is specific to the test case? Thanks
n is not specific to the test case. Look again, n is the size of the array. You are confusing it with the maximum integer of the array which would in fact be specific to the test case.
Yes, you can also say that the answer is dp[n]. In fact, dp[100000] will be equal to dp[n], because freq[i] (for i > n) will be 0 and therefore the value of dp[n] will propagate upwards to n=100000.
What about this case:
The answer could be dp[8] or dp[100000], but dp[3] doesn't work. I don't think anything in the problem statement implies that n is greater than the maximum element.
Thanks for explanation.It is very helpful for me.
In the tutorial of Problem 456B - Fedya and Maths
I can't really understand the transformation of the equation if anyone can explain.
we know from modulo theory examples : 3%5=-2%5, 4%5=-1%5 so new equation is - (1)^n+(2)^n+(3)^n+(4)^n=(1)^n+(2)^n+(-2)^n+(-1)^n - so for n==odd answer is simply "0" for n==even which are multiple of 4 answer is =4 and for n==even which is not multiple of 4 ans is zero. take a pen and paper do some work on it you can get that idea and the complexity of this solution is O(1) .
for the problem 1, going by logic of tutorial and so many other solutions, Alex should be happy for the following data set: (2 1) (3 4) But we can see clearly, it is not so. Am I missing anything?. Thanks.
Limitations: 1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n. Your data set is incorrect.
In the editorial of problem D div2, Consider the example 2 1 abas abacaba now the player one can win and loose the game. so win[root]=true and loose[root]=true.so according to editorial its answer should be first.But the answer is second.Let's consider these moves a--b--a--s using this prefix the player 2 will win? Can anyone explain this to me??
From my debug printing of my AC submission:
Starting player can FORCE win? false , can FORCE lose? falseSecond``In fact, if we merge the two given strings we get something like this:
aba — s \ caba
There are only two possible games. Both share the initial "aba" prefix. The starting player must pick the second a, so the non-starting player can force a win (by choosing the "s") or a lose (by choosing the "c"). So, the starting player outcome only depends on what the non-starting one decides. In this case, we have k = 1, so the Second player can directly win. In fact, in this case the optimal strategy for the second player is winning every game, since the loser player will be the starting one.
In the test you given win[root]=false and lose[root]=false. Check that again!
Correct me if I am wrong. the above test case can be written as Let' name them:_________________________________________________________________________________ (1)a--(2)b--(3)a--(4)s _______________|_____________________________________________________ __________________(5)c--(6)a--(7)b--(8)a
Now in the 4th node
win[4]=false
win[3]=true
win[2]=false
win[1]=true
similarly
loose[8]=true
loose[7]=false
loose[6]=true
loose[5]=false
loose[4]=true
loose[3]= loose[4]|loose[5] =true
loose[2]=false
loose[1]=true
would anyone like to explain for problem E DIV-1 how we got this relation Function is calculated as follows: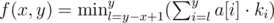 , ki — how many times we visited the i th element of the array a.
, ki — how many times we visited the i th element of the array a.
i understand it :)
netman in your code of Problem E of DIV 1 Can you explain the algorithm of function addline() and mergeCHs() ,how these function works ? it will be great help !!! sorry for my bad english
addLine() — it is adding line to Convex Hull. In my structure all lines are in decreasing order of K. And we can easily add line to structure in O(1) operations. You can draw a lines in the order of decreasing K to better understand this.
If our lines are in decreasing order of K in structure, we can easily merge 2 structures. Add all lines in decreasing order to new structure in O(n + m) operations, where n and m — sizes of 2 structures.
Read this article to better understand.
netman in your addline() function the first if condition you do this bb=max(b[l-1],bb) i did not get the idea why you did this . please explain it
Ohh... sorry... In right solution must be bb=min(b[l-1],bb).
Tests very weak and my solution with this bug passed tests :(
Can anyone give me detail explain for solution of problem D div 1 ?
I agree. Your English is very bad :P. But can you please make someone else post in English? I cannot understand the tutorials properly. :(
opening solution 7452418 of PROBLEM 455E — FUNCTIONS shows "you are not allowed to view the requested page". Why is that? Please fix it! Thanks
netman can you please tell what does f(i) denote in the editorial for problem C of Div2.?
f(i) — maximal sum if we delete all numbers that smaller or equal to i.
thanks :)
netman if it is so, then how would f(n) give answer to original problem, as any number lies between 1 and 10^5 and is also independent of value of n.
there could be a test case like
So, I think the answer should be f(max(a[i])) [for all i in range(1, n)]
Please correct me if I am wrong. I am quite weak at DP.
You are right =)
Answer is f(maxA).
Can someone please explain 456C — Boredom / 455A — Boredom ?
According to what I understood, the above statement does the following:
f(i-1)Here the numberi-1is selected at some point number which removes all the occurrences of the numberi, hence there is no termcnt[i]·if(i-2)+cnt[i]·iHere the numberi-2is selected at some point which removes all the occurrences of numberi-1and then we are separately removing all the occurrences of the numberiwhich is the termcnt[i]·iThen we are taking the maximum of the above two calculated values.
But it can be possible that we do not select the number
i-1inf(i-1)and also we do not select the numberi-2inf(i-2).So how is this correct? Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks
Can someone please explain 456C — Boredom / 455A — Boredom ?
According to what I understood, the above statement does the following:
f(i-1)Here the numberi-1is selected at some point number which removes all the occurrences of the numberi, hence there is no termcnt[i]·if(i-2)+cnt[i]·iHere the numberi-2is selected at some point which removes all the occurrences of numberi-1and then we are separately removing all the occurrences of the numberiwhich is the termcnt[i]·iThen we are taking the maximum of the above two calculated values.
But it can be possible that we do not select the number
i-1inf(i-1)and also we do not select the numberi-2inf(i-2).So how is this correct? Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks
Lets say that the numbers are contained in an array of srtucts a[], and it is sorted by the number in it.
That struct contains the current number and time it is writen.
The idea is that there is no sense to chose f(i-2), without chosing "i" too, because all numbers are >= 0. So we will either chose the current (ith) number or we will skip it. That means if(a[i-1].numb == a[i].numb-1) we must call a rec(i-2) + a[i].numb * a[i].cnt, because we already deleted all (a[i]-1) elements. But if(a[i-1].numb != a[i].numb-1) => there are no elements equal to a[i] — 1 and that means we can simply call rec(i-1) + a[i].numb * a[i].cnt. If we want to skip the current element we just call rec(i-1).
From this => rec(i) = max(rec(i-1), ((a[i].numb == a[i-1].numb + 1) ? rec(i-2) : rec(i-1)) + a[i].numb * a[i].cnt)
And after that you need just to do memoization.
EDIT: The answer will be rec(N). Let the the array be 1-indexed ans rec(0) = 0, rec(1) = a[1].numb*a[1].cnt.
Thank you very much for your explanation :)
Can someone please explain this test case in 455A ?
5
4 2 3 2 5
how this output is 9?
choose any 2 -> delete 3
choose another 2
choose 5 -> delete 4
total 9
how many times i have to choose?
In this case just 3 times (2,2,5). But anyway number of choosing doesn't really matter to optimal choosing. We can get optimal value by more than one way
My solution for Div. 2 B is much simpler. Check if the number is divisible by 4 (check the last two digits), if it is divisible then the answer is 4. Otherwise the answer is 0. I don't know how to prove it but I got Accepted.
In C, n should actually be max[a[i]]
can someone explain problem D more gracefully , like more of explanation with simple words? (sqrt decomposition method)
Divide an array into blocks. For each block, you have cnt[block_id][x] -> how many x's we have in this block. To do a shift operation, you need to delete last element and insert it before first one. To delete and insert element, you can find where this element is located and delete it (this will take O(sqrt(N)) because size of each block is O(sqrt(N))). But after several queries, some blocks will be too small and some will be too large. That's why you need fully re-construct your sqrt-decomposition after some number of queries.
how can we mantain which element is last in the block the block? i think this will consume o(n) , beacause as we perform a cycle shift , a new element acquires the new position. I was thinking about keeping sqrt(n)queues and then for a shift we always a sqrt operations .. what say?
Look, let us have a two arrays: vector all[numberOfBlocks] and also cnt[numberOfBlocks][maxNumber] to maintain information in blocks. How to do a shift operations? Shift operation is deleting R'th number and inserting it in L'th position.
Now we need insertion and deletion functions.
Take a look at my insertion:
By doing the shift, we change the sizes of blocks. After N queries, some blocks can have no element, while others have O(N) elements. But to make our blocks as close to sqrt(N) as possible, we can totally re-build our decomposition every sqrt(N) queries.
Rebuild is something like this:
After re-building, all blocks will have size of O(sqrt(N)).
Div 1 Problem D: I don't understand the need for the array
wasVals[][]in the author's solution 7407693. Its only use is to setmet[block][value]=0.Couldn't this be done using the array
vals[][]. Will there be a scenario wheremet[block][value]>0andvals[block][]does not contain thevalue?Edit: I just removed wasVals[][] from author's code and it works 17138498. So looks like it is not needed.
Sorry but i missed the problem limitation 1<= a[i],b[i] <= n
this was my original comment :D
problem A maybe i miss understood something about the problem statement or solution.. or there is something wrong with the solution..
Sample Input:
2
1 2
2 3
Solution Output:
Happy Alex
because there exists a pair of a[i],b[i] where a[i]!=b[i] but it's wrong due to problem statement we need to find laptop having less price and higher quality..
Sorry for the long run :D
You saved me man, i was also getting frustrated on this, guess i also missed this 1<= a[i],b[i] <= n
Glad to hear so :D
Can anyone please explain the logic behind tourist's solution: 7390969 for Div 1, D. Serega and Fun problem. It would be of great help. Thanks in advance.
не разбор, а херня
I am new to competitive programming, can anybody tell why my submission to Boredom is showing time limit exceeding error in eleventh testcase ?
submission to Boredom is showing time limit exceeding error in eleventh testcase ?
Also, I don't understand the syntax used in the official C++ solution for boredom, but how you create a array containing the number of occurrence of each elements on O(n) time ?
Don't use Diagnostics compiler.
For Div2E / Div1C, how can one prove the formula for the new diameter? $$$Diameter_{new} = max(Diameter_u, Diameter_v, \left \lceil{\frac{Diameter_u}{2}}\right \rceil + \left \lceil{\frac{Diameter_v}{2}}\right \rceil + 1)$$$
I understand that in the case that the merged part is not connected to the previous diameter, and is not large enough to affect the diameter, it will be the previous diameter, but how do you prove the last part? I know that it is for the case when the two diameters are going to be connected, but cannot fully understand / prove it. How does it ensure that the diameter is minimum? Why does taking half always work?
Div1.C statement make me confuse @@ "Between any pair of cities there either is a single (unique) PATH, or there is no path at all". I don't think graph is forest until I see editorial ><
I was trying to solve 456C — Boredom / 455A — Boredom. I wrote the code and it works correctly. The issue is that it shows signed integer overflow for case 42. I have already tried using unsigned long long int but still the problem persists. Moreover, I've seen other codes with no use of long long or anything of that sort. Any help would be appreciated ! Here's my code : https://codeforces.com/problemset/submission/455/75532685
Try changing
int arr[mx]={0};tounsigned long long arr[mx]={0};as $$$i * arr_i$$$ can be as big as $$$1e10$$$.The given n doesn't fit in long long for DIV2B. Getting WA on C++14. Changed to pypy3 and AC!!
For Div2 D / Div1 B look at this comment.
An important point in fedys and maths problem missed by the tutorial setters is that if the result of n % 4 is equal to 0 then the answer is 4 otherwise it is 0. There is no need to do any kind of binary exponentiation or any other mode of fast exponentiation.
in 456-A laptops if we give following input it should return poor alex according to the problem statement but according to your solution and the solution that is accepted it is printing happy alex. input I gave- 2 1 2 2 3
Can anyone show the proof of finding the diameter of two merged components in DIV 1C?
To get the minimum diameter after merging, one should always merge two components from the middle node of their respective diameter paths which explains $$$\left \lceil{\frac{Diameter_u}{2}}\right \rceil + \left \lceil{\frac{Diameter_v}{2}}\right \rceil + 1$$$. Then we should check if any individual component's diameter is greater than it or not.
Thanks, I works.
for problem E — civilization do we need to connect the centroid of 2 components which are to be merged , so that our new diameter would be minimum as possible.
[Sorry for necroposting]
lol Overkilled the Div. 1 C with small to large merging + $$$O(n)$$$ memory binary lifting from https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/74847.
I've got the observation that the new diameter can be obtained by connecting two middle points of two trees, also got the observation that the new diameter is whether to connect the two trees' diameter pair, or the old diameter pair of both trees.
Didn't know that the diameter will always be sum of ceil of both. So I coded the online merging lca-able tree sets that maintains the diameter pair.
231305622
Is it possible to use recursion/memoization for 456C — Boredom / 455A — Boredom? No matter what I do I am getting stack overflows on larger test cases. I figure most DP problems should be able to be solved with both Top-down as well as bottom-up approaches but I am also new to CF so this may be be wrong on my part.
yes
https://codeforces.com/contest/455/submission/51869347
Sorry for necroposting, don't want to create a separate post for this.
Don't understand why I am getting WA 249969116. It's almost identical to the tutorial. I think most probably it is some stupid bug, but I'm not able to figure it out even after spending a good time on it. I wonder if the reason is the pointer implementation as opposed to the 2D table one.
Nice!!
Ala ho Akhabar