Statistics
Total Users/Teams who have made a submission: 754
Total Submissions: 4212
Number of distinct users/teams with correct submissions: 498
Winners
The Editorials of the following problems are prepared by me, aditya1495 and harshil.
Shil and RasenShuriken
(setter: harshil)
Total number of pairs such that their product is even. Count total number of odd numbers = x.
Product of two numbers is odd if the both numbers are odd.
Ans = N*(N-1)/2 — x*(x-1)/2
Shil Loves Exclusive Or
(setter: harshil)
Use the fact that Xor of 2x and 2x+1 is 1.
Therefore xor of 1 to 4n+3 is 0.
You can derive the appropriate answer from the following results
F(4n+3) = 0
F(4n) = 4n
F(4n+1) = 4n ^ (4n+1) = 1
F(4n+2) = (4n+2)^1
Utkarsh and Random Trees
(setter: usaxena95)
Dp[i] = expected distance of node i from root.
Dp[i] = 1 + 0.5*(Dp[i-1] + Dp[i-2])
Also an observation is that the height of the tree is equal to the distance of node N from 1.
Therefore ans = Dp[N].
Complexity O(N + T)
This is invalid if problem is to randomly take one of last 3 nodes as parent of i. So Dp[i] = 1 + (Dp[i-1] + Dp[i-2] + Dp[i-3]) / 3 remains analogous. But expected height is not same as Dp[N].
Same Old Matrix Problem
(setter: aditya1495)
Solving this problem required considering some cases.
First we will generate 2 DP Tables:
1.) dp[i][j] = Maximum money I can collect, moving only right or down and travelling from (1, 1) to (i, j).
2.) rdp[i][j] = Maximum money I can collect, moving from (i, j) to (N, M).
We can solve the problem using above two DP tables and splitting the possible scenarios in 6 different cases.
Let variable RES store your answer. Initialise RES with dp[N][M], as you are sure to make this profit without any change in direction.
Consider the following images for clarity.
Red arrow is the move obtained by paying P dollars. Two green arrows indicate moves before and after the move with red arrow. Which one is taken before and which one is after can easily be understood.
Case 1:
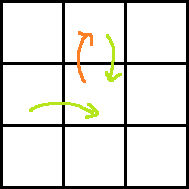
Ans: dp[i][j] + A[i − 1][j + 1] + rdp[i][j + 1] − P
Case 2:
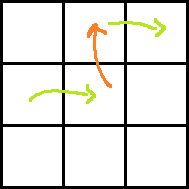
Ans: rdp[i − 1][j + 2] + dp[i][j] + A[i][j + 1] + A[i − 1][j + 1] − P
Case 3:
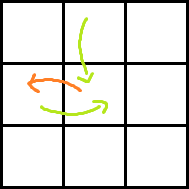
Ans: dp[i][j] + A[i + 1][j − 1] + rdp[i + 1][j] − P
Case 4:
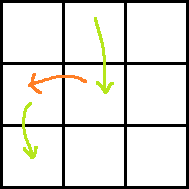
Ans: rdp[i + 2][j − 1] + dp[i][j] + A[i + 1][j − 1] + A[i + 1][j] − P
Case 5:
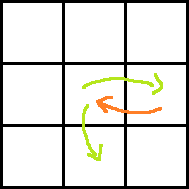
Ans: dp[i][j] + rdp[i + 1][j] + A[i][j + 1] − P
Case 6:
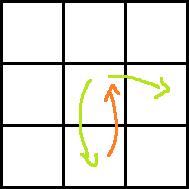
Ans: dp[i][j] + rdp[i][j + 1] + A[i + 1][j] − P
Take maximum of RES with Ans for all valid cells (i, j) for all valid cases.
Note: Don't forget that you cannot move out of grid. So make sure that A, dp, and rdp values exist for required positions before processing a case. Also since money in cell can be negative, make sure that you initialize dp and rdp with −INF. Many code made this mistake and got a penalty.
Utkarsh and Sub Array Sum
(setter: usaxena95) How to calculate F(A) efficiently ? Lets consider the ith bit. Let the number of elements in A who has ith bit ON be x. Number of elements whose ith bit is OFF be y = N-x. Xor of a sequence of bits is 1 if the total number of 1's are odd. Number of sub sequences whose xor sum has ith bit ON = number of sub sequences having odd number of 1.
This can calculated by combinatorics = (Take any number of 0's)*(take odd number of 1's) = (2x)*(yC1 + yC3 + yC5 +..+) = (2x) * (2y-1) = 2x+y-1 = 2N-1. We add this to answer if y ≥ 1. Which means that add 2N-1 to ans if OR of ith bits of A is 1 (i.e. y ≥ 1)
Result: F(A) depends only on the length of A and Bitwise Or of all the elements of A.
F(A) = OR * 2N-1 where N = size of A. So the problem was reduced to efficiently calculating the value of OR of a subarray and also deal with updates. This can be done easily with segment trees.
Complexity = O(N + Q * LogN) (Solution by karanaggarwal)
If you consider each bit individually, solution will be O(30 * Q * logN) BIT will get TLE.
Utkarsh and Tree Labelling
(setter: usaxena95) This was supposed to be a cumbersome hurdle which had a subtle solution.
One way to solve it is
- Do a DFS order
- Travel in reverse order
- You need to know the sum of all the unique elements in the range L..R
- This can be done as in DQUERY using BIT and map storing the last occurrence of a all values.
Another way to solve it storing for each node v all the unique values of F in the subtree of v in a set S[v] similar to problem Knapsack on Tree which is discussed later.
A very simple observation to make is that value of F[v] just depends on the distance of the node v from the farthest leaf present in the subtree of v. Quite a few participants were able to notice this and were able to finish subtly in 40-60 LOC.
How can we prove this formally? Proof by induction:
Base case: The value of F[v] is 0 for all leaves. If Height H = 0 then F[v] is fixed = 0.
Assume for any node u whose height is ≤ H has F[u] dependent on just H (i.e. F[u] = someFunction(Height(u)) )
Induction step: Consider node v with height = H + 1. Let v have children u1, u2,..un. It means that some children ux's must have height = H. Other children will have height < H. As subtree of ux contains nodes of all the heights from 1 to H, all those children of v whose height is < H are useless as their F[u] value must have been present in value of some node in subtree of ux. (using induction step that F[u] is independent of connectivity of graph and just dependent on height of u if height ≤ H).
As the other children do not contribute to the calculation of v, we can just focus on child ux. As F[ux] is a function of only H and only this child will contribute to calculation of F[v], therefore F[v] = is a function of only H+1.
We can precalc the answer for any height H as Pre[H].
if(Pre[i-1] is repeated in prefix i) then Pre[i] = Pre[i-1] + (Pre[H-1]+1) * 2Pre[H-1] mod M
else Pre[i] = Pre[i-1]
Complexity O(N + H*LogH) (Solution by gvaibhav21) O(N) from dfs. H = height of root.
Shil and Special XorSum
(setter: harshil)
In this problem we were required to find Σ RMQ(i,j) ^A[i]^A[j] where i<j. RMQ(i,j) gives max of all the elements from i to j.
We will use divide and conquer approach for this problem. Suppose we are currently at state (l,r) , lets find m such that A[m] = max(A[l],A[l+1]..A[r]) and l ≤ m ≤ r. If there are many such m, pick anyone. This can be found easily using segment trees.
Now we will process for every bit position from 0 to 19. Suppose we are considering jth bit. We will find total number of pairs (p,q) such that l ≤ p ≤ m ≤ q ≤ r and jth bit is on in A[m]^A[p]^A[q].
Let l1 be total number of positions in [l,m] having jth bit on and l0 be total number of positions in [l,m] having jth bit off. Similarly let r1 be total number of positions in [m,r] having jth bit on and r0 be total number of positions in [m,r] having jth bit off.
If jth bit is on in A[m] , then total number of such (p,q) pairs is (l1*r1 + l0*r0 -1 ). If jth bit is off in A[m] , then total number of such (p,q) pairs is (l1*r0 + l0*r1 -1). Hence we will add in answer 2j*(l1*r1 + l0*r0 -1 ) in first case and 2j *(l1*r0 + l0*r1 -1 ) in second case.
Then we will move forward to state (l,m-1) and (m+1,r). Solution complexity is O(N*logN +N*20).
See the solution for more understanding and implementation details:solution by PrashantM
The recursive solution I explained is implemented in iterative way in above solution.
Knapsack on Tree
(Setters: architkarandikar, usaxena95 and aditya1495)
We are given a bound that no subset can have move than A[v] nodes from subtree rooted at node v. Hence if A[v] <= Size of subtree at v, then we have to choose the A[v] nodes have largest B values from subtree at v.
Lets maintain a Set for each node which stores valid nodes from it's subtree. If the Size of Set[v] exceeds A[v], then we'll remove smallest (Size of Set[v] — A[v]) nodes from Set[v]. Now to generate the Set[v], we'll use Set[x] for all x such that v is a parent of x. Note that if a node in subtree of x is not present in Set[x], then it will also be absent from Set[v] too and so on for all the ancestors. Hence we have to generate Set[v] by merging all the Set[x] and take A[v] largest elements in Set[v]. Then our answer would be elements of Set[1]. We can iterate on Set[1] and take summation of B values of its elements and that would be the answer.
Doing this plainly would be O(n^2 log n) which won't fit in in time limit. We need some smarter way of doing this.
To generate Set[v] of any node v, we'll first recognize the heavy child of this node. Heavy child would be the one which has largest size of it's Set (We'll refer as Heavy Set). We can then iterate on all the Light children and insert their elements in this Heavy Set. This Heavy set would now contain the nodes of subtree at v, the largest A[v] of which are required for Set[v]. We can resize Heavy set to contain the largest A[v] elements and now, instead of wasting time in copying those elements in Set[v], we can simply make a note that "If you want to see Set[v], see this Heavy set instead". This can be done by maintaining a 1-1 mapping using an array or using pointers and making the pointer of Set[v] point to this Heavy set.
Hence, we have now reduced O(n^2 log n) to O(n log^2 n) which fits perfectly in time limits! Ta-da!
Better Purchases
(Setter aditya1495)
This question is solvable by modelling it as a Minimum Cost Flow Network. Since it was a bipartite graph, min-cost matching can be used. Constraints are such that we need O(n^3) solution. We can use, for example Hungarian Algorithm which fits in time.
M = Number of shelves
N = Number of Companies
C[i] = Capacity of ith shelf
X[i] = Free goods that company i provides
Y[i] = Charged goods that company i provides
P[i] = Price per unit of charged good of Company i
We need some basic greedy things to clear out before we proceed. First step would be to sort the shelves in decreasing order of their capacities. Then if M > N, we'll take largest N shelves else we'll have to use all M. Let M' = min(M, N). We'll take largest M' shelves. Also, we'll take free goods from a company first and then only charged goods.
Assume that total number of goods you will order is sum of capacities all the M' shelves i.e. fill all shelves completely. Lets name it MaxGoods. We'll reduce it by counting the empty slots remaining at the end. Now, connect each company with the each shelf with flow capacity 1 and cost being as follows:
Cost[i][j] => if (X[i] + Y[i] <= C[j]) then Y[i] * P[i] + (C[j] − X[i] − Y[i]) * INF
if (X[i] < C[j]) then (C[j] − X[i]) * P[i]
if (X[i] >= C[j]) then 0
You can choose INF value greater than Sum (P[i] * Y[i]). Constraints permitted INF = 10^9. Here (C[j] − X[i] − Y[j]) indicates the amount of free slots that will remain if we match company i with shelf j. We "charge" such a match INF for each empty slot it creates, since we want to utilize maximum space (and hence maximum goods!).
Finding the min-cost match will give Flow = M' (obvious!). Useful part here would be the value of Cost. Since our matching will try to minimize total cost, it will try matching Companies-Shelves such that INF is used as less as possible and hence maximize goods in shelves. So the number of free slots that will be there in the end will be number of INF that you can reduce from Cost i.e Cost / INF. All the remaining cost will be contributed by charged goods. So actual cost will be Cost % INF. (% is modulo operation).
So finally, the number of goods that we could purchase is:
PurchasedGoods = MaxGoods − EmptySlots = MaxGoods − Cost / INF.
TotalCost = Cost % INF.
Note that we are doing integer division in Cost / INF.
Many coders tried some greedy approaches which failed system test cases. Proof of failure of greedy approach is out of the scope of this write-up (unfortunately). Hence it is left as an exercise for reader. But a brute-force solution and a test generator can do the trick in case you need such a case.
Shil and Shortest Path
(setter harshil)
In this problem , we need to find lexicographical Kth shortest path from 1 to N. Let d[i] be the length of shortest path from any node i to N and dp[i] be total number of shortest path from any node i to N. Both of these can be found easily using BFS. Now we will build the lexicographical Kth string step wise. On each step, we will decide which character to add at the end of our current string. Final string formed after processing all such steps will be our lexicographical Kth shortest path string. Hence we will make d[1] such steps.
Let STATE denotes array of all the nodes we are processing in our current step. Initially, STATE will contain only node 1. On jth step, STATE will contain all the nodes having their shortest path distance from N equal to d[1]-j+1 and that could lie on lexicographical K th shortest path.While moving for next step, we will build new STATE array and forgot our previous STATE array.At last step, STATE will contain only last node N.
In each step, we will iterate from 'a' to 'z' until we have found the character that should be included in our string at jth step. When we find that any particular character c should be included in our string, we will add it to the string and move to j+1 th step. Now lets see how to decide that character c should be included in our string or not at certain jth step.
In any particular step , we will iterate on all the nodes U present in our STATE array.For each node U , consider all nodes V adjacent to U such that d[V]=d[U]-1 and label of edge (U,V) is c. Let S denotes the total number of all the shortest path containing the edge (U,V) and their previous edges having the labels we have included in the string till now. If S>=K , we will include character c in our string , else we will subtract S from K and move to c+1 character.After we have decided that we should include certain character c in our string , we have to build new STATE array before moving to next step.This new STATE array can be build by inserting all the nodes V such that there exist edge (U,V) where U is present in our previous state , d[V]=d[U]-1 and label of edge (U,V) is c. For calculating S and dp , we have to take special care to check for overflow since total number of shortest path in any graph could be very high.See the solution for seeing how to calculate S and implementation details.
Feel free to discuss your own strategies of solving the problems in the comments. :D









Auto comment: topic has been updated by usaxena95 (previous revision, new revision, compare).
DZ16TREE is still not available in the practice area.Can you move it in to the practice area?
DZ16TREE is still not in practice area...please move it!!
Auto comment: topic has been updated by usaxena95 (previous revision, new revision, compare).
How complexity of Knapsack on Tree comes to be O(nlog2n) ?
Each time, you merge the smaller multiset into the larger one. Consider any arbitrary P[i] value. Every time you remove it from a certain multiset and insert it into some other, the size of the merged multiset is atleast twice the size of the original.
Say you merge multisets x and y. Assume size(x) ≤ size(y). Therefore, by the algorithm, you will push all the elements of x into y. Let xy be the merged multiset. size(xy) = size(x) + size(y). But size(y) ≥ size(x). So size(xy) ≥ 2 * size(x).
Thus, each value cannot be moved more than log n times. Since each move is done in O(logn), the total complexity for n values amounts to O(nlog2 n)
usaxena95 thanks for Editorials. In Shil and Special XorSum, I could not understand that why you did -1 in
then total number of such (p,q) pairs is (l1*r1 + l0*r0 -1 ). Won't it be(l1*r1 + l0*r0 )? I am not able to figure out why you did -1thanks for cool problems.
for problem C — Utkarsh and Random Trees : how you prove formula ? I know +1 part reason , but 0.5*(Dp[i-1] + Dp[i-2]) is what I can't understand it's correctness.
Node i connects with node i - 1 and node i - 2 with equal probability. Hence it's level will be dp[i - 2] + 1 with probability 0.5 and dp[i - 1] + 1 with probability 0.5.
Using linearity of expectation,
dp[i] = 0.5 * (dp[i - 1] + 1) + 0.5 * (dp[i - 2] + 1) = 0.5 * (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]) + 1.
In Utkarsh and Tree Labelling:
What is a DFS order? Is it the same as a Euler Tour so that a subtree can be represented as a range of an array?
After the DFS order, what is the significance of travelling in reverse order?