→ Pay attention
→ Top rated
| # | User | Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ecnerwala | 3650 |
| 2 | Benq | 3582 |
| 3 | Geothermal | 3570 |
| 3 | orzdevinwang | 3570 |
| 5 | cnnfls_csy | 3569 |
| 6 | tourist | 3565 |
| 7 | maroonrk | 3532 |
| 8 | Radewoosh | 3522 |
| 9 | Um_nik | 3483 |
| 10 | jiangly | 3468 |
→ Top contributors
| # | User | Contrib. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | maomao90 | 174 |
| 2 | awoo | 164 |
| 3 | adamant | 163 |
| 4 | TheScrasse | 159 |
| 5 | nor | 158 |
| 6 | maroonrk | 156 |
| 7 | -is-this-fft- | 151 |
| 8 | SecondThread | 147 |
| 9 | orz | 146 |
| 10 | pajenegod | 145 |
→ Find user
→ Recent actions
Codeforces (c) Copyright 2010-2024 Mike Mirzayanov
The only programming contests Web 2.0 platform
Server time: Apr/23/2024 13:07:50 (j2).
Desktop version, switch to mobile version.
Supported by
User lists

| Name |
|---|



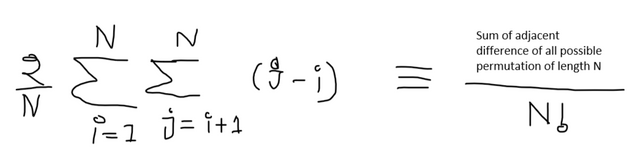






Nice drawing :D
What's that character in brackets after summations before i (?-i)
I don't know if this convince you.
Let's assume the difference is taking an absolute sign. There are $$$n!$$$ permutation of len $$$n$$$. For one permutation there are $$$n-1$$$ adjacent difference. The probability of getting one pair $$$(x,y)$$$ or $$$(y,x)$$$ , having the difference $$$|x-y|$$$ is $$$\frac{2}{n(n-1)}$$$
So the sum will be $$$N! (N-1) \frac{2}{N(N-1)} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \sum_{j=1+1}^{N} (j-i) = N! \frac{2}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \sum_{j=1+1}^{N} (j-i)$$$