You are given two even integers $$$n$$$ and $$$m$$$. Your task is to find any binary matrix $$$a$$$ with $$$n$$$ rows and $$$m$$$ columns where every cell $$$(i,j)$$$ has exactly two neighbours with a different value than $$$a_{i,j}$$$.
Two cells in the matrix are considered neighbours if and only if they share a side. More formally, the neighbours of cell $$$(x,y)$$$ are: $$$(x-1,y)$$$, $$$(x,y+1)$$$, $$$(x+1,y)$$$ and $$$(x,y-1)$$$.
It can be proven that under the given constraints, an answer always exists.
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line of input contains a single integer $$$t$$$ ($$$1 \le t \le 100$$$) — the number of test cases. The following lines contain the descriptions of the test cases.
The only line of each test case contains two even integers $$$n$$$ and $$$m$$$ ($$$2 \le n,m \le 50$$$) — the height and width of the binary matrix, respectively.
For each test case, print $$$n$$$ lines, each of which contains $$$m$$$ numbers, equal to $$$0$$$ or $$$1$$$ — any binary matrix which satisfies the constraints described in the statement.
It can be proven that under the given constraints, an answer always exists.
32 42 24 4
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
White means $$$0$$$, black means $$$1$$$.
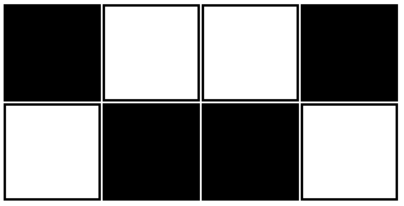 | 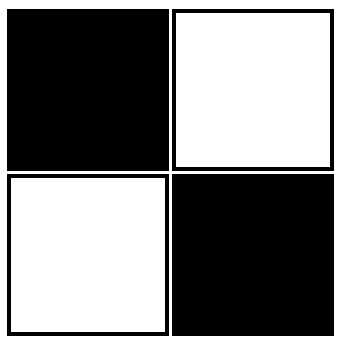 | 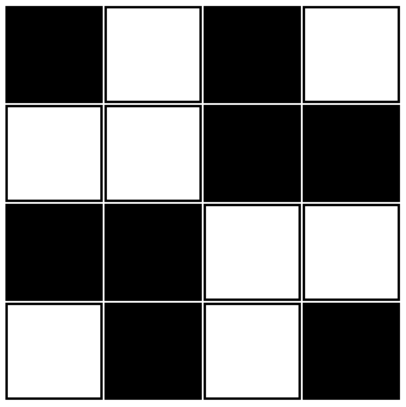 |
| The binary matrix from the first test case | The binary matrix from the second test case | The binary matrix from the third test case |