The segment tree is a very useful algorithm when doing many RMQ problems, we have the following problem:↵
https://codeforces.com/contest/1199/problem/D↵
how to solve it?↵
Well, here is the segment tree to help us, but what is the segment tree?↵
Well, it is a tree where each node is F(x, y) being x and y stored in its 2 children↵
here is an example and the implementation:↵
↵
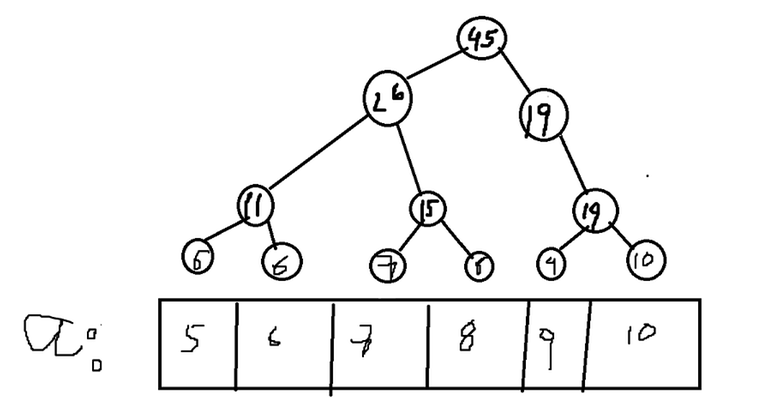↵
↵
~~~~~↵
#include <bits/stdc++.h>↵
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>↵
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>↵
#ifdef LOCAL↵
#include "debug/debug.h"↵
#include "float/floatx.hpp"↵
#include "ttmath/ttmath.h"↵
#include "json/json.hpp"↵
#include <omp.h>↵
#include <unistd.h>↵
#include <windows.h>↵
using namespace flx;↵
using namespace ttmath;↵
using namespace nlohmann;↵
using namespace literals;↵
#include "win/api.hpp"↵
#endif↵
#ifndef LOCAL↵
#define debug↵
#endif↵
#define pb push_back↵
#define ll long long↵
#define ld long double↵
#define fx ld // antes estaba otra cosa↵
#define ull unsigned ll↵
#define S second↵
#define F first↵
using namespace std;↵
using namespace chrono;↵
using namespace __gnu_pbds;↵
#define THREAD_NUM 32↵
#define MOD 1000000007↵
const ll INF = 1e18, MAXN = 5e5 + 10;↵
↵
typedef tree<ll, null_type, less_equal<ll>,↵
rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update>↵
TREE;↵
↵
ll a[MAXN], st[MAXN * 4], lazy[MAXN * 4];↵
↵
ll F(ll a, ll b)↵
{↵
return a + b;↵
}↵
↵
void build(ll n, ll l, ll r)↵
{↵
lazy[n] = 0;↵
if (l == r)↵
{↵
st[n] = a[l];↵
return;↵
}↵
ll m = (l + r) / 2;↵
build(n * 2, l, m);↵
build(n * 2 + 1, m + 1, r);↵
st[n] = F(st[n * 2], st[n * 2 + 1]);↵
}↵
↵
void prop(ll l, ll r, ll n)↵
{↵
st[n] += lazy[n] * (r - l + 1);↵
if (l != r)↵
{↵
lazy[n * 2] = lazy[n];↵
lazy[n * 2 + 1] = lazy[n];↵
}↵
lazy[n] = 0;↵
}↵
↵
void update(ll n, ll l, ll r, ll a, ll b, ll val)↵
{↵
prop(l, r, n);↵
if (l > b || r < a)↵
return;↵
if (l >= a && r <= b)↵
{↵
lazy[n] += val;↵
prop(l, r, n);↵
return;↵
}↵
ll m = (l + r) / 2;↵
update(n * 2, l, m, a, b, val);↵
update(n * 2 + 1, m + 1, r, a, b, val);↵
st[n] = F(st[n * 2], st[n * 2 + 1]);↵
}↵
↵
ll query(ll n, ll l, ll r, ll a, ll b)↵
{↵
prop(l, r, n);↵
if (l > b || r < a)↵
return 0;↵
if (l >= a && r <= b)↵
return st[n];↵
ll m = (l + r) / 2;↵
ll q1 = query(n * 2, l, m, a, b);↵
ll q2 = query(n * 2 + 1, m + 1, r, a, b);↵
return F(q1, q2);↵
}↵
↵
int main(){↵
int n;↵
cin >> n;↵
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){↵
cin >> a[i];↵
}↵
build(1,1,n);↵
int q;↵
cin >> q;↵
while(q--){↵
//process query ↵
}↵
}↵
~~~~~
https://codeforces.com/contest/1199/problem/D↵
how to solve it?↵
Well, here is the segment tree to help us, but what is the segment tree?↵
Well, it is a tree where each node is F(x, y) being x and y stored in its 2 children↵
here is an example and the implementation:↵
↵
↵
↵
~~~~~↵
#include <bits/stdc++.h>↵
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>↵
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>↵
#ifdef LOCAL↵
#include "debug/debug.h"↵
#include "float/floatx.hpp"↵
#include "ttmath/ttmath.h"↵
#include "json/json.hpp"↵
#include <omp.h>↵
#include <unistd.h>↵
#include <windows.h>↵
using namespace flx;↵
using namespace ttmath;↵
using namespace nlohmann;↵
using namespace literals;↵
#include "win/api.hpp"↵
#endif↵
#ifndef LOCAL↵
#define debug↵
#endif↵
#define pb push_back↵
#define ll long long↵
#define ld long double↵
#define fx ld // antes estaba otra cosa↵
#define ull unsigned ll↵
#define S second↵
#define F first↵
using namespace std;↵
using namespace chrono;↵
using namespace __gnu_pbds;↵
#define THREAD_NUM 32↵
#define MOD 1000000007↵
const ll INF = 1e18, MAXN = 5e5 + 10;↵
↵
typedef tree<ll, null_type, less_equal<ll>,↵
rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update>↵
TREE;↵
↵
ll a[MAXN], st[MAXN * 4], lazy[MAXN * 4];↵
↵
ll F(ll a, ll b)↵
{↵
return a + b;↵
}↵
↵
void build(ll n, ll l, ll r)↵
{↵
lazy[n] = 0;↵
if (l == r)↵
{↵
st[n] = a[l];↵
return;↵
}↵
ll m = (l + r) / 2;↵
build(n * 2, l, m);↵
build(n * 2 + 1, m + 1, r);↵
st[n] = F(st[n * 2], st[n * 2 + 1]);↵
}↵
↵
void prop(ll l, ll r, ll n)↵
{↵
st[n] += lazy[n] * (r - l + 1);↵
if (l != r)↵
{↵
lazy[n * 2] = lazy[n];↵
lazy[n * 2 + 1] = lazy[n];↵
}↵
lazy[n] = 0;↵
}↵
↵
void update(ll n, ll l, ll r, ll a, ll b, ll val)↵
{↵
prop(l, r, n);↵
if (l > b || r < a)↵
return;↵
if (l >= a && r <= b)↵
{↵
lazy[n] += val;↵
prop(l, r, n);↵
return;↵
}↵
ll m = (l + r) / 2;↵
update(n * 2, l, m, a, b, val);↵
update(n * 2 + 1, m + 1, r, a, b, val);↵
st[n] = F(st[n * 2], st[n * 2 + 1]);↵
}↵
↵
ll query(ll n, ll l, ll r, ll a, ll b)↵
{↵
prop(l, r, n);↵
if (l > b || r < a)↵
return 0;↵
if (l >= a && r <= b)↵
return st[n];↵
ll m = (l + r) / 2;↵
ll q1 = query(n * 2, l, m, a, b);↵
ll q2 = query(n * 2 + 1, m + 1, r, a, b);↵
return F(q1, q2);↵
}↵
↵
int main(){↵
int n;↵
cin >> n;↵
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){↵
cin >> a[i];↵
}↵
build(1,1,n);↵
int q;↵
cin >> q;↵
while(q--){↵
//process query ↵
}↵
}↵
~~~~~





