It was easy realization problem. Let's increase the variable i from 1 to n, and inside let's increase the variable j from 1 to 2·m. On every iteration we will increase the variable j on 2. If on current iteration a[i][j] = '1' or a[i][j + 1] = '1' let's increase the answer on one.
Asymptotic behavior of this solution — O(nm).
Let's calculate the answer to every block separately from each other and multiply the answer to the previous blocks to the answer for current block.
For the block with length equals to k we can calculate the answer in the following way. Let for this block the number must be divided on x and must not starts with digit y. Then the answer for this block — the number of numbers containing exactly k digits and which divisible by x, subtract the number of numbers which have the first digit equals to y and containing exactly k digits and plus the number of numbers which have the first digit equals to y - 1 (only if y > 0) and containing exactly k digits.
Asymptotic behavior of this solution — O(n / k).
The main proposition to solve this problem — in the middle of every competition the sensor must be or in the top point of the wheel or in the bottom point of the wheel.
To calculate the answer we need to use binary search. If the center of the wheel moved on the distance c, then the sensor moved on the distance c + rsin(c / r), if the sensor was on the top point of the wheel in the middle, or on the distance c - rsin(c / r), if the sensor was on the bottom point of the wheel in the middle, where r — the radius of the wheel.
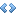
Asymptotic behavior of this solution —  .
.
Let's find the centers of every rectangle and multiple them of 2 (to make all coordinates integers).Then we need to by the rectangle door, which contains all dots, but the lengths of the sides of this door must be rounded up to the nearest integers.
Now, let's delete the magnets from the door one by one, gradually the door will decrease. Obviously every time optimal to delete only dots, which owned to the sides of the rectangle. Let's brute 4k ways, how we will do delete the magnets. We will do it with helps of recursion, every time we will delete point with minimum or maximum value of the coordinates. If we will store 4 arrays (or 2 deques) we can do it with asymptotic O(1). Such a solution works O(4k).
It can be easily shown that this algorithm delete always some number of the leftmost, rightmost, uppermost and lowermost points. So we can brute how k will distributed between this values and we can model the deleting with helps of 4 arrays. This solution has asymptotic behavior O(k4).
To calculate the answer on every query let's use the formula 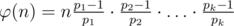 , where p1, p2, ..., pk — all prime numbers which divided n. We make all calculations by the module 109 + 7
, where p1, p2, ..., pk — all prime numbers which divided n. We make all calculations by the module 109 + 7
Let's suppose that we solving problem for fix left end l of the range. Every query now is a query on the prefix of the array. Then in formula for every prime p we need to know only about the leftmost position of it. Let's convert the query in the query of the multiple on the prefix: at first init Fenwick tree with ones, then make the multiplication in points l, l + 1, ..., n with value of the elements al, al + 1, ..., an. For every leftmost positions of prime p make in position i the multiplication in point i on the 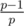 . This prepare can be done with asymptotic
. This prepare can be done with asymptotic 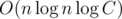 , where C — the maximum value of the element (this logarithm — the number of prime divisors of some ai).
, where C — the maximum value of the element (this logarithm — the number of prime divisors of some ai).
We interest in all leftmost ends, because of that let's know how to go from the one end to the other. Let we know all about the end l — how to update the end l + 1? Let's make the multiplication in the Fenwick tree in the point l on the value al - 1. Also we are not interesting in all prime numbers inside al, so let's make the multiplications in point l on the all values 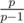 . But every of this prime numbers can have other entries which now becoming the leftmost. Add them with the multiplication which described above. With helps of sort the transition between leftmost ends can be done in
. But every of this prime numbers can have other entries which now becoming the leftmost. Add them with the multiplication which described above. With helps of sort the transition between leftmost ends can be done in 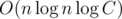 .
.
To answer to the queries we need to sort them in correct order (or add them in the dynamic array), and to the get the answer to the query we will make 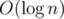 iterations. So total asymptotic behavior of solution is
iterations. So total asymptotic behavior of solution is 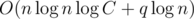 iterations and
iterations and 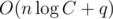 additional memory.
additional memory.
Опишем жадный алгоритм, который позволяет решить задачу при k > 2 для любой строки S.
Будем считать, что мы всегда переворачиваем некоторый префикс строки S (возможно, длины 1, подробнее ниже). Поскольку мы стремимся минимизировать строку лексикографически, легко убедиться в том, что мы будем переворачивать такие и только такие префиксы, префикс которых (после переворачивания) совпадает с минимальным лексикографически суффиксом перевернутой строки S (обозначим ее Sr), в частности, это префикс, совпадающий по длине с минимальным суффиксом Sr (операция переворачивания префикса S равносильна замене его суффиксом Sr соответствующей длины).
Обозначим минимальный лексикографически суффикс строки Sr как s. Можно показать, что никакие два вхождения s в Sr не пересекаются, так как в противном случае строка s была бы периодической, и минимальный суффикс имел бы меньшую длину. Значит, строка Sr имеет вид tpsaptp - 1sap - 1tp - 2... t1sa1, где sx означает конкатенацию строки s x раз, a1, a2, ..., ap — натуральные числа, а строки t1, t2, ..., tp — некоторые непустые (кроме, возможно, tp) строки, не содержащие s в качестве подстроки.
Перевернув некоторый подходящий префикс строки S, мы перейдем к меньшей строке S', при этом минимальный суффикс s' этой перевернутой строки S'r не может быть лексикографически меньше, чем s (это каждый может доказать самостоятельно), поэтому мы стремимся сделать так, чтобы s' осталось равным s, что позволит увеличить префикс вида sb в ответе (а значит и минимизировать его). Легко доказать, что максимальное b, которое мы можем получить, равно a1 в случае p = 1 и 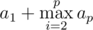 (в случае, если p \geq 2$). Действительно, после таких операций префикс ответа будет выглядеть как sa1saitisai - 1... sa2t2. Поскольку t_{i} — непустые строки, увеличить количество конкатенаций s в префиксе ответа никак не получится. Заметим, что переворот второго префикса (sai...) возможен, так как k > 2.
(в случае, если p \geq 2$). Действительно, после таких операций префикс ответа будет выглядеть как sa1saitisai - 1... sa2t2. Поскольку t_{i} — непустые строки, увеличить количество конкатенаций s в префиксе ответа никак не получится. Заметим, что переворот второго префикса (sai...) возможен, так как k > 2.
Из описанных выше утверждений следует, что при k > 2 для оставшейся строки всегда следует переворачивать префикс, который после переворота совпадает с суффиксом строки Sr вида sa1. Чтобы находить этот суффикс каждый раз, достаточно один раз построить декомпозицию Линдона (с помощью алгоритма Дюваля) перевернутой исходной строки и аккуратно объединять равные строки в ней. Единственным случаем остается вариант, когда префикс оставшейся строки переворачивать не нужно — его можно обработать как конкатенацию последовательных переворачиваемых префиксов длины 1.
Поскольку для k = 1 задача тривиальна, осталось решать задачу для k = 2, то есть деление строки на две части (префикс и суффикс) и какой-то способ их переворачивания. Случай, когда ничего не переворачивается, нам не интересен, рассмотрим два других случая:
Префикс не переворачивается. В таком случае обязательно переворачивается суффикс. Два варианта строки с перевернутым суффиксом можно сравнивать за O(1) с помощью z-функции строки Sr#S.
Префикс переворачивается. Для решения этого случая можно воспользоваться утверждениями из разбора задачи F Яндекс.Алгоритма 2015 из Раунда 2.2 авторства GlebsHP и рассмотреть только два варианта поворота префикса, перебрав для каждого из них все два варианта поворота суффикса.
Остается выбрать из двух случаев лучший ответ. Итоговая асимптотика решения O(|s|).