710A - King Moves
Easy to see that there are only three cases in this problem. If the king is in the corner of the board the answer is 3. If the king is on the border of the board but not in a corner then the answer is 5. Otherwise the answer is 8.
Complexity: O(1).
710B - Optimal Point on a Line
The function of the total distance is monotonic between any pair of adjacent points from the input, so the answer is always in some of the given points. We can use that observation to solve the problem by calculating the total distance for each point from the input and finding the optimal point.
The other solution uses the observation that the answer is always is the middle point (by index) in the sorted list of the given points. The last fact is also can be easily proven.
Complexity: O(nlogn).
710C - Magic Odd Square
The problem was suggested by Resul Hangeldiyev Resul.
The solution can be got from the second sample testcase. Easy to see that if we place all odd numbers in the center in form of rhombus we will get a magic square.
Complexity: O(n2).
710D - Two Arithmetic Progressions
I wanted to give this problem a lot of time ago. I thought it is very standard problem, but I underestimated its difficulty.
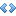
Let's write down the equation describing the problem: a1k + b1 = a2l + b2 → a1k - a2l = b2 - b1. So we have linear Diofant equation with two variables: Ax + By = C, A = a1, B = - a2, C = b2 - b1. The solution has the form: 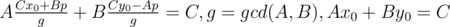 , where the last equation can be solved by extended Euclid algorithm and p is any integral number. The variable p should satisfy two conditions:
, where the last equation can be solved by extended Euclid algorithm and p is any integral number. The variable p should satisfy two conditions: 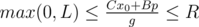 and
and 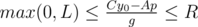 . The values A and B are fixed, so we can get the segment of possible values for the values p. The length of the segment is the answer for the problem.
. The values A and B are fixed, so we can get the segment of possible values for the values p. The length of the segment is the answer for the problem.
Complexity: O(log(max(a1, a2))).
710E - Generate a String
The problem was suggested by Zi Song Yeoh zscoder.
This problem has a simple solution described by participants in the comments.
My solution is a little harder. Let's solve it using dynamic programming. Let zn be the smallest amount of time needed to get n letters 'a'. Let's consider transitions: the transition for adding one letter 'a' can be simply done. Let's process transitions for multiplying by two and subtraction by one simultaneously: let's decrease the number 2·i i times by one right after getting it. Easy to see that such updates never include each other, so we can store them in queue by adding the new update at the tail of the queue and taking the best update from the head.
The solution is hard to describe, but it is very simple in the code, so please check it to understand the idea :-)
Complexity: O(n).