| Codeforces Round 864 (Div. 2) |
|---|
| Finished |
Li Hua has a tree of $$$n$$$ vertices and $$$n-1$$$ edges. The root of the tree is vertex $$$1$$$. Each vertex $$$i$$$ has importance $$$a_i$$$. Denote the size of a subtree as the number of vertices in it, and the importance as the sum of the importance of vertices in it. Denote the heavy son of a non-leaf vertex as the son with the largest subtree size. If multiple of them exist, the heavy son is the one with the minimum index.
Li Hua wants to perform $$$m$$$ operations:
- "1 $$$x$$$" ($$$1\leq x \leq n$$$) — calculate the importance of the subtree whose root is $$$x$$$.
- "2 $$$x$$$" ($$$2\leq x \leq n$$$) — rotate the heavy son of $$$x$$$ up. Formally, denote $$$son_x$$$ as the heavy son of $$$x$$$, $$$fa_x$$$ as the father of $$$x$$$. He wants to remove the edge between $$$x$$$ and $$$fa_x$$$ and connect an edge between $$$son_x$$$ and $$$fa_x$$$. It is guaranteed that $$$x$$$ is not root, but not guaranteed that $$$x$$$ is not a leaf. If $$$x$$$ is a leaf, please ignore the operation.
Suppose you were Li Hua, please solve this problem.
The first line contains 2 integers $$$n,m$$$ ($$$2\le n\le 10^{5},1\le m\le 10^{5}$$$) — the number of vertices in the tree and the number of operations.
The second line contains $$$n$$$ integers $$$a_{1},a_{2},\ldots ,a_{n}$$$ ($$$-10^{9}\le a_{i}\le 10^{9}$$$) — the importance of each vertex.
Next $$$n-1$$$ lines contain the edges of the tree. The $$$i$$$-th line contains two integers $$$u_i$$$ and $$$v_i$$$ ($$$1\le u_i,v_i\le n$$$, $$$u_i\ne v_i$$$) — the corresponding edge. The given edges form a tree.
Next $$$m$$$ lines contain operations — one operation per line. The $$$j$$$-th operation contains two integers $$$t_{j},x_{j}$$$ ($$$t_{j}\in \{1,2\}$$$, $$$1 \leq x_{j} \leq n$$$, $$$x_{j}\neq 1$$$ if $$$t_j = 2$$$) — the $$$j$$$-th operation.
For each query "1 $$$x$$$", output the answer in an independent line.
7 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 3 6 6 7 1 6 2 3 1 6 1 2
2 3 3
10 14 -160016413 -90133231 -671446275 -314847579 -910548234 121155052 -359359950 83112406 -704889624 145489303 1 6 1 10 10 8 1 4 3 4 2 7 2 5 3 2 9 8 1 4 2 2 2 4 1 4 1 10 2 10 1 9 1 6 2 8 2 10 1 5 1 8 1 1 2 5
-2346335269 -314847579 -476287915 -704889624 121155052 -1360041415 228601709 -2861484545
In the first example:
The initial tree is shown in the following picture:
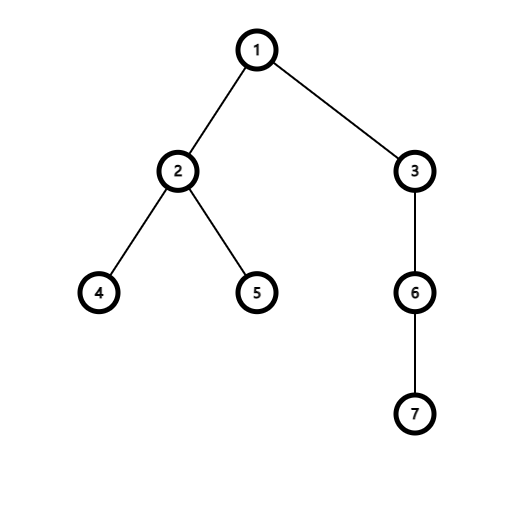 |
The importance of the subtree of $$$6$$$ is $$$a_6+a_7=2$$$.
After rotating the heavy son of $$$3$$$ (which is $$$6$$$) up, the tree is shown in the following picture:
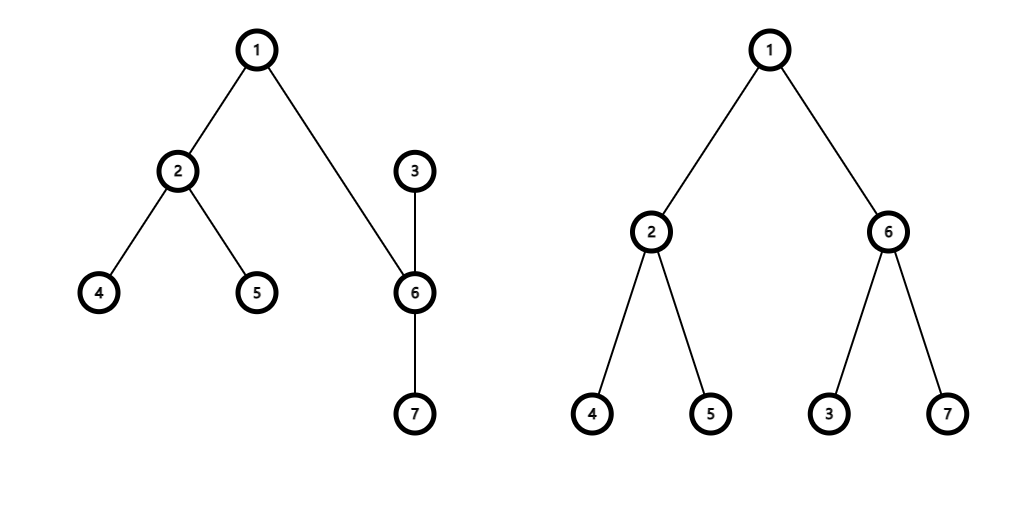 |
The importance of the subtree of $$$6$$$ is $$$a_6+a_3+a_7=3$$$.
The importance of the subtree of $$$2$$$ is $$$a_2+a_4+a_5=3$$$.
| Name |
|---|




