| Codeforces Round 465 (Div. 2) |
|---|
| Закончено |
Известно, что древние египтяне использовали большой набор символов 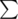 для письма на стенах храмов. Фафа и Фифа подошли к одному из таких храмов и нашли два непустых слова S1 и S2 равной длины, написанные одно под другим. Поскольку храм очень древний, некоторые символы стерлись со временем. На позиции каждого из стертых символов изначально мог стоять любой символ из множества
для письма на стенах храмов. Фафа и Фифа подошли к одному из таких храмов и нашли два непустых слова S1 и S2 равной длины, написанные одно под другим. Поскольку храм очень древний, некоторые символы стерлись со временем. На позиции каждого из стертых символов изначально мог стоять любой символ из множества 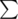 с равной вероятностью.
с равной вероятностью.
Фифа задал Фафе задачу посчитать вероятность того, что слово S1 лексикографически больше слова S2. Можете помочь Фафе решить ее?
Вы знаете, что 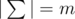 , т. е. всего египтяне использовали m различных символов, которые в этой задаче обозначены целыми числами от 1 до m в порядке следования в алфавите. Слово x лексикографически больше слова y той же длины, если до некоторой позиции эти слова совпадают, а затем в слове x идет буква с большим номером в алфавите, чем в слове y.
, т. е. всего египтяне использовали m различных символов, которые в этой задаче обозначены целыми числами от 1 до m в порядке следования в алфавите. Слово x лексикографически больше слова y той же длины, если до некоторой позиции эти слова совпадают, а затем в слове x идет буква с большим номером в алфавите, чем в слове y.
Можно показать, что искомая вероятность равна 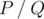 , где P и Q — взаимно простые числа, и
, где P и Q — взаимно простые числа, и 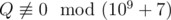 . Выведите в качестве ответа величину
. Выведите в качестве ответа величину 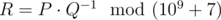 , т. e. такое целое неотрицательное число, меньшее 109 + 7, что
, т. e. такое целое неотрицательное число, меньшее 109 + 7, что 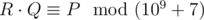 , где запись
, где запись 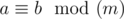 означает, что a и b дают одинаковые остатки от деления на m.
означает, что a и b дают одинаковые остатки от деления на m.
Первая строка содержит два целых числа n и m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105) — длина обоих слов и размер алфавита 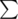 , соответственно.
, соответственно.
Вторая строка содержит n целых чисел a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ m) — символы в слове S1. Если ai = 0, то символ на позиции i стерт.
Третья строка содержит n целых чисел, описывающих S2 в том же формате, что и S1.
Выведите величину 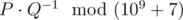 , где P и Q — взаимно простые, и
, где P и Q — взаимно простые, и 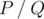 равняется искомой вероятности.
равняется искомой вероятности.
1 2
0
1
500000004
1 2
1
0
0
7 26
0 15 12 9 13 0 14
11 1 0 13 15 12 0
230769233
В первом примере первое слово могло изначально быть (1) или (2). Второй способ — единственный, при котором первое слово лексикографически больше второго. Поэтому ответ равен 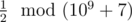 , что есть 500000004, потому что
, что есть 500000004, потому что 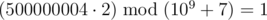 .
.
Во втором примере ни один способ заменить ноль на символ во втором слове не сделает первое слово лексикографически больше второго. Поэтому ответ на задачу равен 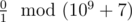 , то есть 0.
, то есть 0.
| Название |
|---|




