Hi guys, Looking codes of reds after contests, i was very curious, because they use random_shuffle() on many cases. But i do not know good aplications for this function.
Can somebody help me with some problems and aplications that is easy solveable with random_shuffle()?
thanks for advice :D











Sometimes you can write a solution that works great for random data, but fails on some several specific test cases. Using random_shuffle kinda eliminates such cases by making data order random. For example quick sort works like that. There can be test when it will work in O(n^2) time, but random_shuffles almost ensures that it's O(n * log(n)). Maybe there are other usecases, but idk about them.
By the way, how to prove that standard quicksort implementation that uses an a[(l + r) / 2] element as a pivot works in expected time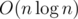 if we apply random_shuffle to the array?
if we apply random_shuffle to the array?
It is a well-known exercise to prove that quicksort with pivot uniformly chosen at random works in expected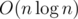 time but I never heard about proving the same statement for a deterministic quicksort after shuffling at random.
time but I never heard about proving the same statement for a deterministic quicksort after shuffling at random.
Let's better choose leftmost element every time. Then you can say that on the first step you have chosen some rank for each element. Then if you choose leftmost element it will be element with the lowest rank in the group. But in each group of elements element with the lowest rank was chosen uniformly due to permutation.
I think kth element in each subset will be chosen uniformly too...
Can you elaborate what is rank?
The place which element has after permutation.
This is correct for the first iteration, though after you run a standard pivot procedure (consider a following model implementation), you must prove that the distribution of a permutation induced by each of the resulting parts of the array is still uniform.
It seems to be true, though.
Well, at least it seems to be correct if sort is implemented as stable :)
How was random shuffle used in 358 div2 . E?we needed to calculate triangle with maximum area ,how random shuffle helps in doing that.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lR-eLHSqAaA
The main idea is that after shuffling the input you can be sure that the order cannot be 'bad' (like in qsort example above).
Sometimes (like in video) it can result in improving complexity.