| Codeforces Round 848 (Div. 2) |
|---|
| Finished |
You are given a rooted tree consisting of $$$n$$$ vertices numbered from $$$1$$$ to $$$n$$$. Vertex $$$1$$$ is the root of the tree. Each vertex has an integer value. The value of $$$i$$$-th vertex is $$$a_i$$$. You can do the following operation at most $$$k$$$ times.
- Choose a vertex $$$v$$$ that has not been chosen before and an integer $$$x$$$ such that $$$x$$$ is a common divisor of the values of all vertices of the subtree of $$$v$$$. Multiply by $$$x$$$ the value of each vertex in the subtree of $$$v$$$.
What is the maximum possible value of the root node $$$1$$$ after at most $$$k$$$ operations? Formally, you have to maximize the value of $$$a_1$$$.
A tree is a connected undirected graph without cycles. A rooted tree is a tree with a selected vertex, which is called the root. The subtree of a node $$$u$$$ is the set of all nodes $$$y$$$ such that the simple path from $$$y$$$ to the root passes through $$$u$$$. Note that $$$u$$$ is in the subtree of $$$u$$$.
The first line contains an integer $$$t$$$ ($$$1 \leq t \leq 50\,000$$$) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $$$n$$$ and $$$k$$$ ($$$2 \leq n \leq 10^5$$$, $$$0 \leq k \leq n$$$) — the number of vertices in the tree and the number of operations.
The second line contains $$$n$$$ integers $$$a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$$$ ($$$1 \leq a_i \leq 1000$$$), where $$$a_i$$$ denotes the value of vertex $$$i$$$.
Each of the next $$$n - 1$$$ lines contains two integers $$$u_i$$$ and $$$v_i$$$ ($$$1 \leq u_i, v_i \leq n$$$, $$$u_i \neq v_i$$$), denoting the edge of the tree between vertices $$$u_i$$$ and $$$v_i$$$. It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $$$n$$$ over all test cases does not exceed $$$2 \cdot 10^5$$$.
For each test case, output the maximum value of the root after performing at most $$$k$$$ operations.
25 224 12 24 6 121 21 32 42 55 324 12 24 6 121 21 32 42 5
288 576
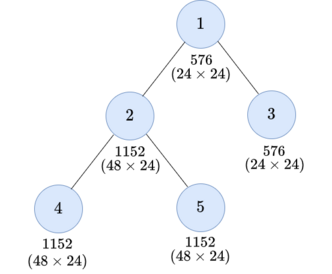
Both examples have the same tree:
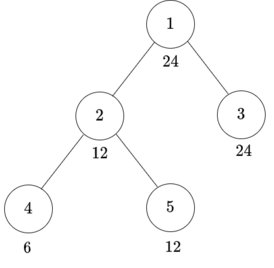
For the first test case, you can do two operations as follows:
- Choose the subtree of vertex $$$4$$$ and $$$x = 2$$$.
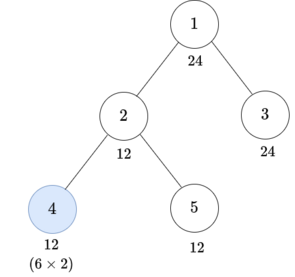
- Choose the subtree of vertex $$$1$$$ and $$$x = 12$$$.
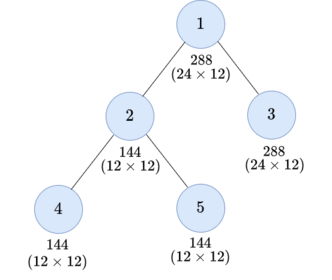
For the second test case, you can do three operations as follows:
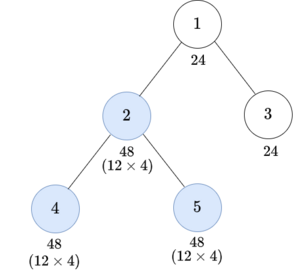
- Choose the subtree of vertex $$$4$$$ and $$$x = 2$$$.

- Choose the subtree of vertex $$$2$$$ and $$$x = 4$$$.
- Choose the subtree of vertex $$$1$$$ and $$$x = 24$$$.
| Name |
|---|




