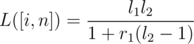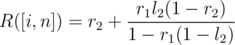Hi everyone, here are the solutions to the contest problems.
712A — Memory and Crow
Note that a[i] + a[i + 1] = b[i]. Use the initial condition b[n] = a[n] and we can figure out the entire array b.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Code#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int arr[100000];
int ans[100000];
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
cin >> arr[i];
}
for(int i = n-1; i >=0; i--){
if(i==n-1) ans[i] = arr[i];
else ans[i] = arr[i] + arr[i+1];
}
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
712B — Memory and Trident
First, if S has odd length, there is no possible string because letters must come in opposite pairs. Now, let's denote the ending coordinate after following S as (x, y). Since S has even length, |x| has the same parity as |y|. Suppose they are both even. Then clearly, we can make x = 0 in exactly 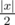 moves, and same for y. If instead they are both odd, then we can change exactly one x-character into a y-character. With the correct choices of these characters, now our string has |x| and |y| with even parity, thus reducing to the problem above. Therefore, the answer is (|x| + |y|) / 2.
moves, and same for y. If instead they are both odd, then we can change exactly one x-character into a y-character. With the correct choices of these characters, now our string has |x| and |y| with even parity, thus reducing to the problem above. Therefore, the answer is (|x| + |y|) / 2.
Time Complexity: O(|S|)
Code#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
if(str.length()%2==1){
cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
int x=0,y=0;
for(int i=0; i < str.length(); i++){
if(str[i]=='U')y++;
if(str[i]=='D')y--;
if(str[i]=='L')x--;
if(str[i]=='R')x++;
}
cout << (abs(x)+abs(y))/2 << endl;
}
712C — Memory and De-Evolution
Let's reverse the process: start with an equilateral triangle with side length y, and lets get to an equilateral triangle with side length x. In each step, we can act greedily while obeying the triangle inequality. This will give us our desired answer.
Time Complexity: O(log x)
Code#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x,y;
cin >> x >> y;
int besta=y,bestb=y,bestc=y;
int turns = 0;
while(true){
//check the current
if(besta>=x && bestb>=x && bestc>=x){
cout << turns << endl;
break;
}
turns++;
if(turns%3==1){
//update a
besta = bestb+bestc-1;
}
if(turns%3==2){
//update b
bestb = besta+bestc-1;
}
if(turns%3==0){
//update c
bestc = besta+bestb-1;
}
}
return 0;
}
712D — Memory and Scores
One approach to this problem is by first implementing naive DP in O((kt)2). The state for this is (diff, turn), and transitions for (diff, turn) is the sum (diff - 2k, turn - 1) + 2(diff - 2k + 1, turn - 1) + 3(diff - 2k + 2, turn - 1) + ... + (2k + 1)(diff, turn - 1) + 2k(diff + 1, turn - 1) + ... + diff( + 2k, turn - 1).
Now, if we use prefix sums of all differences in (turn-1), along with a sliding window technique across the differences, we can cut a factor of k, to achieve desired complexity O(kt2).
However, there is a much nicer solution in O(kt log kt) using generating functions(thanks to minimario). We can compute the coefficients of 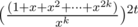 , and the coefficient to xi corresponds to the number of ways we can form the difference i. To compute these coefficients, we can use the binomial theorem.
, and the coefficient to xi corresponds to the number of ways we can form the difference i. To compute these coefficients, we can use the binomial theorem.
Time Complexity: O(kt2)
Code
#include <bits\stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int MOD = 1000000007;
long long dp[2][1000000];
int lowest;
int h(int v){
return v - lowest;
}
int main()
{
int a,b,k,t;
cin >> a >> b >> k >> t;
int lowb = a-b;
int highb = a-b;
lowest = lowb - 2*k*(t);
dp[0][h(lowb)] = 1l;
//solve for ti = 0
int curr = 1;
for(int p = lowb-2*k; p<= lowb; p++){
dp[1][h(p)] = curr;
curr++;
}
curr--;
for(int p = lowb+1; p<= lowb+2*k; p++){
curr--;
dp[1][h(p)] = curr;
}
lowb -=2*k;
highb+=2*k;
for(int ti = 1; ti <= t-1; ti++){
int o = ti%2;
vector<long long> pref;
pref.push_back(dp[o][h(lowb)]);
long long su = dp[o][h(lowb)];
for(int p = lowb+1; p <= highb; p++){
su = (su+dp[o][h(p)])%MOD;
pref.push_back(su);
}
int pe = 2*k;
int il = 0;
int ir = 0;
int l = lowb;
int r = lowb;
int np = lowb-2*k;
long long sum = 0;
//get the prefix first
while(ir<=2*k){
//evaluate current
sum = (sum + pref[ir])%MOD;
dp[!o][h(np)] = sum;
//update for the next thing
ir++;
r++;
np++;
}
pe = 0;
ir--;
r--;
np--;
while(pe<2*k){
pe++;
ir++;
r++;
np++;
//evaluate
sum = (sum + pref[ir])%MOD;
sum = (sum - 2*pref[pe-1])%MOD;
sum = (sum+MOD)%MOD;
dp[!o][h(np)] = sum;
}
//slide into those dm's
while(r<highb){
//update
pe++;
r++;
l++;
ir++;
il++;
np++;
long long sum1 = pref[pe-1] - ( (il==1) ? 0 : pref[(il-1)-1]);
long long sum2 = pref[ir] - pref[pe-1];
sum = (sum - sum1 + MOD)%MOD;
sum = (sum + sum2)%MOD;
dp[!o][h(np)] = sum;
}
//finally, suffix
while(l<highb){
l++;
il++;
pe++;
np++;
//subtract [l-1,pe-1]
long long sum1 = pref[min(pe-1,ir)] - ((il==1) ? 0 : pref[il-1-1]);
sum = (sum - sum1 + MOD)%MOD;
if(pe>ir){
}
else{
long long sum2 = pref[ir]-pref[pe-1];
sum = (sum + sum2)%MOD;
}
dp[!o][h(np)] = sum;
}
lowb-=2*k;
highb+=2*k;
}
long long ans = 0;
int o = t%2;
for(int p = 1; p <= highb; p++){
ans = (ans+dp[o][h(p)])%MOD;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
Time Complexity: O(kt log kt)
Code#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef vector<int> vi;
#define f first
#define s second
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define FOR(i, a, b) for (int i=a; i<b; i++)
#define F0R(i, a) FOR(i, 0, a)
const int MAX = 1000005;
const int MOD = 1000000007;
int f[MAX];
int fi[MAX];
int pos(int a) { return ((ll)a%MOD+MOD)%MOD; }
int add(int a, int b) { return ((ll)a+(ll)b)%MOD; }
int sub(int a, int b) { return pos(a-b); }
int mult(int a, int b) { return (ll)pos(a)*b%MOD; }
int sq(int a) { return (ll)a*a%MOD; }
int expo(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) { return 1; }
if (b%2) { return mult(a, sq(expo(a, b/2))); }
else { return sq(expo(a, b/2)); }
}
int inv(int a) { return expo(a, MOD-2); }
int c(int n, int k) {
return mult(f[n], mult(fi[k], fi[n-k]));
}
int poly1[MAX];
int pref2[MAX];
int main() {
f[0] = fi[0] = 1;
FOR(i, 1, MAX) { f[i] = mult(f[i-1], i); fi[i] = inv(f[i]); }
int a, b, k, t;
cin >> a >> b >> k >> t;
if(b-a > 2*k*t){
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
F0R(i, 2*t+1) { poly1[(2*k+1)*i] = ((i%2==0)?1:-1)*c(2*t, i); }
F0R(i, MAX) { pref2[i] = c(2*t-1+i+1, 2*t); }
int lb = 2*k*t+b-a+1;
int ub = 4*k*t;
int ans = 0;
F0R(i, 2*t+1) {
int l = lb-(2*k+1)*i;
int u = ub-(2*k+1)*i;
if (u < 0) { break; }
if (l < 0) { ans = add(ans, mult(poly1[(2*k+1)*i], pref2[u])); }
else { ans = add(ans, mult(poly1[(2*k+1)*i], sub(pref2[u], pref2[l-1]))); }
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
712E — Memory and Casinos
Lets think about two segments of casinos [i, j] and [j + 1, n]. Let L([a, b]) denote the probability we dominate on [a, b], and let R([a, b]) denote the probability we start on b and end by moving right of b. Let
l1 = L([i, j]),
l2 = L([j + 1, n]),
r1 = R([i, j]),
r2 = R([j + 1, n]).
You can use a geometric series to figure out both L([i, n]) and R([i, n]) using only l1,l2,r1, and r2. To derive these series, think about the probability we cross over from j to j + 1 once, twice, three times, and so on. The actual formulas are,
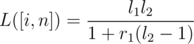
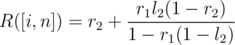
Now we can build a segment tree on the casinos, and use the above to merge segments.
Time Complexity: O(N + QlogN)
Code#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
double pr[100000];
pair<double,double> seg[400000];
bool ze(double d){
return (abs(d) <= 0.0000000001);
}
pair<double,double> merge(pair<double,double> a, pair<double,double> b){
if(ze(a.first+1) && ze(a.second+1)) return b;
if(ze(b.first+1) && ze(b.second+1)) return a;
double l1 = a.first;
double r1 = a.second;
double l2 = b.first;
double r2 = b.second;
if(ze(((l2-1)*r1+1))) return make_pair(0,0);
double le = l1*l2/((l2-1)*r1+1);
double ri = r2+(r1*l2*(-r2+1))/(-r1*(-l2+1)+1);
return make_pair(le,ri);
}
void build(int no, int b, int e){
if(b==e){
seg[no] = make_pair(pr[b],pr[b]);
return;
}
int mid = (b+e)/2;
build(2*no,b,mid);
build(2*no+1,mid+1,e);
seg[no] = merge(seg[2*no],seg[2*no+1]);
}
void upd(int no, int b, int e, int i, double val){
if(i<b || i>e) return;
if(b==e){
seg[no] = make_pair(val,val);
return;
}
int mid = (b+e)/2;
upd(2*no,b,mid,i,val);
upd(2*no+1,mid+1,e,i,val);
seg[no] = merge(seg[2*no],seg[2*no+1]);
}
pair<double,double> query(int no, int b, int e, int l, int r){
if(b>r || e<l) return make_pair(-1,-1);
if(l<=b && e<=r) return seg[no];
int mid = (b+e)/2;
return merge(query(2*no,b,mid,l,r),query(2*no+1,mid+1,e,l,r));
}
int main(){
int q;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
int a,b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
pr[i] = (double)a / (double)b;
}
build(1,0,n-1);
for(int que = 0; que < q; que++){
int ty;
int a;
int b;
scanf("%d %d %d", &ty, &a, &b);
if(ty==1){
int c;
scanf("%d", &c);
upd(1,0,n-1,a-1, (double)b / (double)c);
}
else{
printf("%.20f\n", query(1,0,n-1,a-1,b-1).first);
}
}
return 0;
}
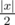 moves, and same for y. If instead they are both odd, then we can change exactly one x-character into a y-character. With the correct choices of these characters, now our string has |x| and |y| with even parity, thus reducing to the problem above. Therefore, the answer is (|x| + |y|) / 2.
moves, and same for y. If instead they are both odd, then we can change exactly one x-character into a y-character. With the correct choices of these characters, now our string has |x| and |y| with even parity, thus reducing to the problem above. Therefore, the answer is (|x| + |y|) / 2.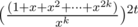 , and the coefficient to xi corresponds to the number of ways we can form the difference i. To compute these coefficients, we can use the binomial theorem.
, and the coefficient to xi corresponds to the number of ways we can form the difference i. To compute these coefficients, we can use the binomial theorem.