Hello codeforces community, I was solving this problem (http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/46425) on codeforces and came across an interesting doubt (at least according to me) . I just wanted to know that is there any algorithm for finding frequency of any number in a particular range in an array?
We use Mo`s Algorithm for finding max frequency in a range but is there any other one which is faster for this particular problem of mine (calculating frequency of any number)?
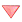
I tried writing an algorithm for it but I believe its too slow to pass in one second. Although I think that my build takes O (n log n) time and queries come out in O (log n) time but I believe it's the uncertainty of hashing that`s making the algorithm slower.
Here is my code — https://pastebin.com/Ypj90749
Note- Please do not tell me the solutions of the codeforces problem. I have already read the editorial and their implementation is pretty simple. I just want to get an answer for my curiosity to be able to learn a new beautiful algorithm (if there is) and help some other learners like me.









Read about merge sort tree it works if there are no updates.
I even thought of this too but I believe it will be even slower than that ( on average ) as it will take o ( log n * log n ) time for answering each query.
log n for first finding node while traversing and other log n for getting the count.
That`s why I used unordered_map so that I am atleast free of the other log n .
I thought of a solution using persistent segment tree. It is also O(nlogn) preprocessing and O(logn) to answer queries.
To build the segment tree, we compress the numbers in the array (using rank). Then, we can loop through the range of ranks and add the numbers in increasing rank to the segment tree (each iteration will add elements of one rank only). Now we have a persistent segment tree, with the kth version being able to answer queries specifying what is the number of elements less than or equal to an element of rank k (in a range). Now to obtain our desired answer, we can simply take:
number of elements in the kth version of the tree — number of elements in the (k-1)th version of the tree.
This will give us the number of elements that are exactly equal to that number (i.e. the number of occurences of that rank k element in the entire array). Now you can just limit the query range to find the frequency of the element within a certain range.
Thanks for taking time for writing this Lance_HAOH but can you please explain a bit more? Persistent segment tree is a completely new data structure for me and I would love if you can explain your solution in a little more easy way.
You can use a vector to store the positions where a number occurs, for each number!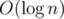 for query. I mean, do
for query. I mean, do 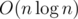 and query
and query 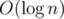 .
.
Then just do Binary Search on the the list of a number to count it's number of occurrences in a range. O(n) Preprocessing and
upperbound(r) - lowerbound(l)on the list of the positions of the number. If there are updates you can use Policy based Data structures (http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/11080). Then PreprocessYour solution is good but I believe if I am having a[i] <= 1e9 , then I will have to use map instead of a vector and things will become O(log n * log n) again.
It will work according to your time complexities only if I have say a[i] <= 1e6.
Am I correct?
Compress the numbers so it will become O(logn) again.
What do you mean by compressing?
I didn`t understand this.
It means each number turnes into his position in the sorted array built from all unique numbers of the given array. So if non-compressed array is defined by A and compressed by B, then for each i, j holds: if A[i] < A[j] (= or >) then B[i] < B[j] (= or > respectively).
As far as the maximum element can't be more than n you can use array B more efficiently and without loss of the relations between elements.
As an example, if A = [38, 100, 100500, 42, 100, 100, 100500], then B = [1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 3, 4].
Why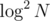 ? One
? One 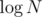 is for access to the map and the next
is for access to the map and the next 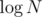 is for binary search, not
is for binary search, not 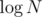 binary searches, isn't it?
binary searches, isn't it?
Oh ya right. Sorry my bad. It will be log (n ^ 2)
Thanks kefaa :)
My implementation according to Rezwan.Arefin01:
If you are allowed to solve it offline (and since you are using Mo's algorithm, I guess you are allowed) then you can do the following:
This should work in O(n + q) if the elements are small enough for array or O(n + q log n) if you need to use map.
Thanks for taking time to help me out ania.
Can you explain point number 2 again or I should say, can you please elaborate it?
I believe explaining things with a live example will be even better :)
Let's say input array is 1 1 2 1 3 and we have queries: X (range=1-2, element=1), Y (range=2-5 element=1) and Z (range=3-5, element=3). Let +X be the upper part and -X the lower part of decomposed query X. In total, we have queries:
The iteration goes as follows:
I believe there is a reason why your contribution in codeforces community is 100 and I have got that :)
This is a beauty, such an amazing explaination :)
Although I will just disturb you for one more thing. You have divided queries into -X and X, what if there are 1e5 queries?
I mean to ask that how to keep a note of it? I think we can use a map < int , set < int > > for this by storing position as key and query number in value (set of that key).
We can probably make two maps for this , with one storing positions to add value and other storing positions to subtract.
I just want to ask if there is any more effective way to do this, because my approach will increase complexity by O(n log n).
I would use array of vectors of queries, where query type is up to your preference. It may be just integer +x or -x, it can be a pair (x,+1) or (x,-1) or even a triple like (x,+1,element). Or you can have two separate arrays of vector for + and for -, like you suggested.
The memory taken is linear because you store only the needed values even though it seems you have nxn array.
That's quite similar to what you want, but you don't need the log from map because keys are up to n. You also don't need the log from set because you process the whole vector/set at once.
oh! you are right :)
Thanks once again ania :) for taking so much time to help a noob like me
Here is my implementation, according to reply of ania..
Thanks for this shahidul_brur
You are most welcome ! It's my pleasure that my code helps you !
hey, can you tell me , how can i find frequencies of all the elements in the given range queries [l,r], most optimally?, it would be thankful if you could help me with the code as you did above .Thanks in advance.
Wavelet Tree.
Woah!Thanks. I never knew about something like that!!