→ Обратите внимание
→ Трансляции
→ Лидеры (рейтинг)
| № | Пользователь | Рейтинг |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | tourist | 3880 |
| 2 | jiangly | 3669 |
| 3 | ecnerwala | 3654 |
| 4 | Benq | 3627 |
| 5 | orzdevinwang | 3612 |
| 6 | Geothermal | 3569 |
| 6 | cnnfls_csy | 3569 |
| 8 | jqdai0815 | 3532 |
| 9 | Radewoosh | 3522 |
| 10 | gyh20 | 3447 |
| Страны | Города | Организации | Всё → |
→ Лидеры (вклад)
| № | Пользователь | Вклад |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | awoo | 161 |
| 2 | maomao90 | 160 |
| 3 | adamant | 156 |
| 4 | maroonrk | 153 |
| 5 | atcoder_official | 148 |
| 5 | -is-this-fft- | 148 |
| 5 | SecondThread | 148 |
| 8 | Petr | 147 |
| 9 | nor | 144 |
| 10 | TheScrasse | 142 |
→ Найти пользователя
→ Прямой эфир
↑
↓
Codeforces (c) Copyright 2010-2024 Михаил Мирзаянов
Соревнования по программированию 2.0
Время на сервере: 27.07.2024 15:12:19 (g1).
Десктопная версия, переключиться на мобильную.
При поддержке
Списки пользователей

| Название |
|---|



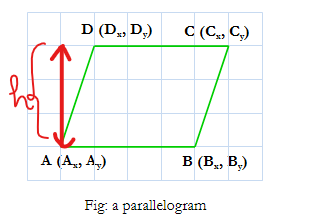







Is is always the case that $$$A_y = B_y$$$ and $$$C_y = D_y$$$? Because in that case it's just $$$D_y-A_y$$$ isn't it.
No. the coordinates can be in different line but ( Ay-By)==( Cy-Dy) are same
I think it should be this
$$$h=\left\lvert \frac{D_x(\frac{B_y-A_y}{B_x-A_x})-D_y-(\frac{A_xB_y-B_xA_y}{B_x-A_x})}{\sqrt{1+(\frac{B_y-A_y}{B_x-A_x})^2}}\right\rvert$$$
This is the general equation independent of what are the constraints on the points(The only thing I have assumed is that the given quadrilateral is a parallelogram). You can make further simplifications in this expression according to the problem.
can you provide the source of that equation? thanks in advance <3
I used some basic coordinate geometry to derive the above equation, you can learn it from the following links
1.Formula to find the equation of a line passing from 2 points: Resource 1
2. Formula to find the perpendicular distance of a point from a line : Resource 2
The basic logic I used was like, I first found the equation of the line AB using the formula given in resource 1 and then I found the perpendicular distance between the line AB and the point D using the formula given in resource 2
Use shoelace theorem. Via shoelace the area is $$$\frac{|(a_x*b_y+b_x*c_y+c_x*d_y+d_x*a_y)-(a_y*b_x+b_y*c_x+c_y*d_x+d_y*a_x)|}{2}$$$. The base is just $$$\sqrt{(a_x-b_x)^2 + (a_y-b_y)^2}$$$ via pythagorean. Then just do the area/base for the height.
Read the topic, he clearly mentions that we have to calculate the height without calculating area.
My bad but the op is interested in the height so that he can calculate the area, and this one finds the area without the height, so I think it's fine.
just figured out that the area and height can be calculated in that way also. Thanks a lot bro.. This really works
Let's say the sides are $$$\vec{AB}$$$ and $$$\vec{AD}$$$, then the height will be $$$AD*sin(\theta)$$$ where $$$\theta$$$ is the angle between $$$\vec{AB}$$$ and $$$\vec{AD}$$$. (We can calculate side vectors from the coordinates)
UPDT: Got the idea now
The area of the parallelogram is the magnitude of the cross product of $$$\overrightarrow{AB} $$$ and $$$ \overrightarrow{AD} = AB\cdot AD\cdot sin(\theta) $$$ so you would directly get the area if that's what you want, but you could then just divide by the base to get the height. The cross product's magnitude is represented in terms of the angle between the two vectors even though it can be calculated with just the coordinates.
See this answer
The angle can be calculated by dot product.
You can get two vectors $$$\overrightarrow{AD} = <D_x-A_x, D_y-A_y>$$$ and $$$\overrightarrow{AB} = <B_x-A_x, B_y-A_y>$$$. The scalar cross product $$$ \overrightarrow {AD} \times \overrightarrow {AB}$$$ is the area of the parallelogram: $$$\mathbf{abs( \left(D_x-A_x\right)\left(B_y-A_y\right)-\left(D_y-A_y\right)\left(B_x-A_x\right) )}$$$