557A — Илья и дипломы
Данную задачу можно решать несколькими способами, рассмотрим один из них — разбор случаев.
Если max1 + min2 + min3 ≤ n, тогда оптимальный ответ (n - min2 - min3, min2, min3).
Иначе, если max1 + max2 + min3 ≤ n, тогда оптимальный ответ (max1, n - max1 - min3, min3).
Иначе, оптимальный ответ (max1, max2, n - max1 - max2).
Данное решение верно, так как по условию задачи гарантируется, что min1 + min2 + min3 ≤ n ≤ max1 + max2 + max3.
Асимптотика решения — O(1).
557B — Паша и чай
Данная задача также может быть решена несколькими способами. Рассмотрим самый простой из них, который укладывается в заданные ограничения.
Сначала отсортируем все чашки по неубыванию их объемов. В силу жадных соображений верно, что отсортированные чашки с номерами от 1 до n будут отданы девочкам, а с номерами от n + 1 до 2 * n будут отданы мальчикам.
Теперь сделаем бинарный поиск с итерациями по объему чая, который будет налит каждой девочке. Пусть на текущей итерации (lf + rg) / 2 = mid. Тогда, если для всех i от 1 до n верно, что mid ≤ ai, а для всех i от n + 1 до 2 * n верно, что 2 * mid ≤ ai, тогда нужно поднять нижнюю границу бинарного поиска, то есть lf = mid. Иначе, нужно опустить верхнюю границу бинарного поиска, то есть rg = mid.
Асимптотика решения — O(n * log(n)), где n — количество чашек.
557C — Артур и стол
Данная задача решается следующим образом. Изначально, отсортируем все ножки по неубыванию их длин. Также нам понадобится массив cnt[].
Переберем длину ножек, на которых будет стоять стол, начиная с наименьшей. Пусть она равна maxlen. Количество единиц энергии, которое нам для этого потребуется будем хранить в переменной cur.
Очевидно, что необходимо открутить все ножки с длинами большими maxlen. Так как массив отсортирован, то, чтобы посчитать количество единиц энергии, которое понадобится для этого, можно воспользоваться суммой энергии на суффиксах. Прибавим это количество к cur.
Если количество ножек длины maxlen не строго больше количества оставшихся ножек, нужно открутить сколько то ножек с длиной меньшей, чем maxlen. Для этого воспользуемся массивом cnt[]. В cnt[i] будем хранить количество ножек со сложностью откручивания равной i. В нем будет содержаться информация о уже рассмотренных ножках.
Будем перебирать сложность откручивания от единицы и откручивать ножки с такими сложностями (прибавляя эти сложности в переменную cur), пока количество ножек с длиной maxlen не станет строго больше количества оставшихся ножек.
Когда ножек длины maxlen станет строго больше половины оставшихся ножек обновим переменной cur ответ.
Асимптотика решения — O(n * d), где n — количество ножек, а d — разность между максимальным и минимальным количеством единиц энергии, которое может понадобится, чтобы открутить какие-то ножки.
557D — Виталий и цикл
Для решения данной задачи нам нужен поиск в ширину или в глубину, который будет проверять каждую компоненту связности графа на двудольность. Очевидно, что количество ребер, которое нужно добавить в граф, чтобы получился нечетный цикл, не превышает трех.
Ответ на задачу равен трем в том случае, когда в графе нет ни одного ребра. Тогда количество способов добавить три ребра в граф, чтобы получился цикл нечетной длины равно количеству способов выбрать три вершины из n (будем соединять ребрами именно эти вершины). Это число равно n * (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 6.
Ответ на задачу равен двум, если в графе нет компонент связности с количеством вершин большим чем два. Как найти количество способов?
Пусть cnt2 — количество компонент связности, которые состоят из двух вершин. Тогда выберем любые две вершины, соединенные ребром. Эти две вершины и ребро, соединяющее их точно войдут в ответ. Осталось выбрать любую другую вершину и соединить ее двумя ребрами с выбранными ранее соединенными вершинами. То есть количество способов равно cnt2 * (n - 2).
Остался случай, когда в графе есть хотя бы одна компонента связности с количеством вершин большим двух. Воспользуемся, например, поиском в глубину для каждой компоненты и будем красить вершины в два цвета. В массиве color[] будем запоминать цвет вершин, изначально все вершины непокрашены.
Пусть в поиске в глубину мы идем из вершины v в вершину to (вершина v уже точно покрашена в какой-то цвет). Если вершина to не покрашена, тогда покрасим ее в цвет, противоположный цвету вершины v и запустим поиск в глубину от вершины to. Если вершина to уже покрашена в цвет, не равный цвету вершины v, пропустим ее. Если же color[v] = color[to], тогда выведем "0 1" и закончим алгоритм. Это означает то, что в графе уже есть цикл нечетной длины.
После запуска поиска в глубину для всех компонент, если не нашлось цикла нечетной длины, нужно добавить лишь одно ребро, чтобы такой цикл получился. Чтобы посчитать количество способов его добавить, нужно проитерироваться по компонентам связности, чей размер больше двух. Все они двудольны, так как нет нечетного цикла в графе.
Если в текущей компоненте связности cnt1 вершин в одной доле и cnt2 вершин в другой доле, тогда к количеству способов нужно прибавить cnt1 * (cnt1 - 1) / 2 и cnt2 * (cnt2 - 1) / 2.
Асимптотика решения — O(n + m), где n — количество вершин в графе, а m — количество ребер.
557E — Аня и полупалиндром
Данная задача решается с помощью динамического программирования.
Сначала насчитаем матрицу good[][]. В good[i][j] запишем true, если подстрока с позиции i до позиции j полупалиндром. Иначе запишем в good[i][j]false. Это можно сделать, перебирая "середину" полупалиндрома и расширяя ее влево и вправо. Возможны 4 случая "середины", но опустим их, так как они достаточно просты.
Теперь будем складывать в бор суффиксы заданной строки. Также будем хранить массив cnt[]. В cnt[v] будем хранить сколько полупалиндромов заканчивается в вершине бора v. Пусть сейчас мы записываем в бор суффикс, который начинается в позиции i, кладем символ, стоящий в строке в позиции j, и переходим в вершину v. Тогда, если good[i][j] = true, нужно сделать cnt[v] + + .
Теперь простым обходом в глубину посчитаем для каждoй вершины sum[v] — сумму чисел, стоящих в вершине v и во всех ее поддеревьях.
Осталось только восстановить ответ. Запустимся из корня бора. Будем хранить его в строке ans. В переменной k храним номер искомой подстроки. Пусть сейчас мы стоим в вершине v, по символу 'a' можем перейти в вершину toa, а по символу 'b' — в вершину tob.
Тогда, если sum[toa] ≤ k, сделаем ans + = 'a' и перейдем в вершину toa. Иначе, нужно сделать следующее: k — = sum[toa], ans + = 'b' и перейдем в вершину tob.
Когда k станет ≤ 0 выведем получившуюся строку ans и закончим алгоритм.
Асимптотика решения — O(szalph * n2), где szalph — размер входного алфавита (в данной задаче он равен двум), а n — длина заданной строки.









You have some Russian (I guess) in "557C — Arthur and Table" 's description.
The russian words can be ignored, the words' meanings are stated in the preceeding words :)
Well, I didn't know that! :)
Taking min of 3 values sounds easier than doing bin.search in B:)
please explain :(
If you give one girl X, then you need n * X for all girls and 2 * n * X for all boys. This means that X < = W / (3 * n), otherwise you'll have not enough water.
You can't give one girl more than ar0, where ar is sorted array from input (because otherwise there will be some tea cup which is too small to give it to some girl).
You can't give one girl more than arn / 2, because this means that you'll have less than n valid tea cups for boys.
So you should simply pick answer according to these 3 restrictions.
Thank you, I understand, I actually did not see that "Pasha pours the same amount of water to each girl"... I thought we could pour any amount of water to any girl :(
auysfdaiuyedwe
Hmmm ... I did exactly that (used fast I/O , sorted using the std::sort in C++ (O(nlog n)) and then checked the conditions) yet got TLE .... The time limit could have been a little relaxed considering it is Div 2 ...
I used same as you and got AC!! seems like there's other problem.
I don't know why you got TLE :( but you are using significantly more memory than necessary, perhaps that made some things slow?
Did you use vector<<double>? I got that TLE when using that too. Changed vector <int> and it worked.
You were trying to input 2*N values into array of size N. AC: 11884732
Due to small array, buffer overflow may have occurred leading to overwriting of value of k and/or i in the For loop. So the for loop may never have exited or taken too long as value of arr[i] can be 10^9 (which gets written into k). Hope this helps :)
I had also done the same but had taken double data type to deal with decimal numbers. Output 1.06798e+008 Answer 106798500.0000000000 Checker Log wrong answer 1st numbers differ — expected: '106798500.0000000', found: '106798000.0000000', error = '0.0000047' How to reduce this error below 10^6 ?
We can even do it more simplified as let say g=a[1] and b=a[n+1] (after sorting 1 based index) then just have 2 conditions if tc = (b*0.5*n+b*n) --> b*0.5 maximum girl cup can have condition being b*0.5 <=g if not so then directly (g*n+2*g*n) is the answer. for case when ans>w take ans=w. that's it :)
Here's my AC code — http://ideone.com/1POnoF
let say you're going to pour x mill in each girls cup
so x <= min{Capacities of girl cups} and 2*x <= min{Capacities of boy cups} --> x <= min{Capacities of boy cups}/2
also, total amount of liquid poured is less than W so, x*n+2x*n = 3x*n <= W --> x<=(W/3n)
Now we distributed n lowest capacity cups to girls and remaining to boys
So x is equal to min{(W/3n),min{Capacities of girl cups}, min{Capacities of boy cups}/2 }
and ans is 3*n*x
I did the same, but along with getting skipped, it also got Wrong answer.
Here is a two-liner (plus rading input and stuff) 11869212, who does exactly this.
Nicely Done. :)
waht?qasdfghjkl;
Недосообразил в задаче D, как найти кол-во способов, если ответ надо добавить 2 ребра. Все моральные свои силы я истратил на задачу C. Обидно:)
wow what a quick editorial compared to the last one :) some statements (in problem C editorial) is still in russian..
quick, but not so good in my opinion. I still don't understand the solution to problem C. How am I supposed to find the sum of energies needed for unscrewing the legs of length smaller then the max.
My solution: - Sort based on height.
- Iterate through the different heights (Consider the ith height as the maximum height)
- This means you have to cut all legs that have length more than i (Use cumulative sum to find that).
- Say the number of legs of length i is k
- You have to leave exactly k-1 legs of height < i. The k-1 legs you leave should have the maximal energies => You have to choose k-1 maximum energy legs whose length are less than i and cut the rest.
- For this I used a map (With a little bit of pre-processing). Iterate from 200 to 0 and while count < k-1.
- While iterating, if there exists a leg of height < i and if count > k-1, decrease count. Else break
- Use cumulative sum to find total energy you have to spend in order to have the ith length as maximum.
- View my submission for further details:
Thank you very much! this helped a ton. You can do it without using a map though.
How to do without a map or any other similar thing (like priority_queue)?
Array
i am getting WA on test case 8. I am using array for storing length from 0 to 200. please help. http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11892251
You declare ans=1000000 which is wrong more than that also possible
Can you please help, i am not able see why my solution is getting wrong answer on test case 8. Here is my solution.
My submisssion
Thnx
Can you please help, i am not able see why my solution is getting wrong answer on test case 8. Here is my solution.
My submisssion
Thnx
Can someone please explain C in more details?
Basically you have to ensure that in remaining legs, frequency of the maximum element is greater than half of number of remaining legs.
We can do this by first choosing the value of maximum element(of remaining legs ). In order to ensure that this is indeed the maximum, we remove all the legs whose length is greater than this value.
After that,we also have to ensure that frequency of the maximum element is greater than half of number of remaining legs. To do this, we remove appropriate number of legs whose length is less than this decided value.
For a given choice of value of maximum element, we can calculate the energy in O(200) by just maintaining the frequency of energy required to remove the legs.
Can u explain how u did this "To do this, we remove appropriate number of legs whose length is less than this decided value." You have to remove weight of ( remaining elements — (no of elements of current leg)/2 — 1 ) elements and these elements should be min possible.
Keep a hash array of energies. So,delete from it the minimum ones. Now after you are done for length 'l',remove all the energies of that value from the hash array(I mean decrement). I kept a list of all energies belonging to a length. You can refer this code.Its sort of documented.
can you please add some more comment in your code for more understanding like what is x.what does this(Removing the maximum leg--check for some other possibility) imply. what are you doing in following lines of code for(j=1;j<210;j++) { if(h2[j]>=r) { temp2+=r*j; break; } else { temp2+=h2[j]*j; r-=h2[j]; } } ans=min(ans,temp2); //~ cout<<"Length "<<i<<" b[i] "<<b[i]<<" remove "<<r<<" Energy "<<temp2<<endl; n-=b[i];
Basically the idea is that whenever you consider length 'l' to be the length of table,then you will have to remove all legs of higher length. That is what I am doing there,removing from my hash table,all energy values of higher lengths. And x & r are just variables. x means if I consider 'l' to be the highest length I will have to keep 2*l -1 legs and remove (r)=n-(2*l -1). Thats the blueprint :) Hope it helps!!
thanks...now i got it..
asdfasd
Very nice explanation friend!! Missed that O(d) thing, just now got it accepted by keeping a hash of energy values after reading your comment. Good work!!
quickest editorial ever :)
quickest editorial ever
Problem statement was not very good. :(
so the array size is the silliest mistake in history, Why the hell did I get TLE instead of RTE for this code !!
Same problem there, had to add Fast IO to get AC.
I got TLE with fast IO too
see the link, I edited it
Try cin/cout with ios:ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false) and cin.tie(NULL); You should get AC.
The array is on the stack, so there's a lot of room to read/write values before you get runtime errors. If N is over 50000, you will overwrite whichever values come after your array (like i), which causes your program to get stuck in the for loop.
F*king precision error!!
same :/
on test 32 right?
same lol.. dropped from top 20% to bottom 30
This is how I solved D.
1st thing to notice was that only 3 edges are sufficient to create an odd cycle.
Case 1: Edges needed 0. Just check if a graph (every component) is bipartite or not. If it is not than the graph contains odd cycle. Ans is (0, 1).
Case 2: Edges needed 1. For this case color every component with 2 colors. Lets say we use A, B to color the nodes. If two nodes have same color than we can add edge between them to create an odd cycle. So ans for this case is (1, naC2 + nbC2) where na is the no.of nodes with color A and nb is the no of nodes with color B. We need to sum this for all components.
Case 3: Edges needed 2. For this case do dfs to count no of components of size 2 and size 1. Ans for this case is (2, 4 * two_cntC2 + two_cnt * (n — 2 * two_cnt)). Every two components of size 2 gives 4 different ways. We also add the ans for the case where individual node components are present which is basically equal to two_cnt * (n — 2 * two_cnt).
Case 4: Edges needed 3. That is every node is disjoint. Ans is (3, nC3).
Edit: Got it! Great question! :D
How do we know that we need edges 1/2/3/0 ? Please see this , i could solve only for the no. of ways( hope it is correct ).
If graph already contains an odd cycle than we don't need to add any edge i.e this is the case where needed edges = 0.
If any component of graph contains more than 2 nodes than we can add 1 edge to create a cycle (this component will not have any odd cycle as we are already considering that case separately).
If the max size of any component in graph is 2 than we need 2 edges to create a cycle. comp1 = A-B, comp2 = C-D to connect these and create odd cycle we need 2 edges.
If graph contains all the nodes separately, i.e max size of any component is 1 than we need 3 edges to create an odd cycle.
I hope it clears your doubt. For reference here is my solution. 11865575
Thanks for the reply :) I have a doubt. Won't above assumptions fail if we have suppose 3 connected components and 1st is bipartite 2nd is not bipartite and third is a simple cycle?
If second component is not bipartite than it contains an odd cycle for which we have already checked. :)
please ignore. made a mistake.
There is already an odd cycle in the given graph. 1,5,6
ashish1610 yeah that was a typing error. I'll check the output again :) sorry for the mistake on my part
My code gives 1 6 for this case. -_-
Second problem was wrong because of a single word; :(
It must have been,
cout<<fixed<<answer; instead of cout<<answer;
used it after contest and got accepted. :(
Does anyone know what parameters to use with printf ? Not sure if I understand the "fixed" option in cout.
printf("%.6lf",answer);
This is just wrong, my submission for B during the contest 11860848
And after the contest the same code along with fast IO 11867502
I spent about an hour trying to debug my solution when there was nothing wrong. Isn't CF supposed to be non-IO centric. This is unfair, Binary search timing out due to Fast IO.
How else are they supposed to give problems with 100000 numbers as input?
Some warning, the very least. Not all of us are reds and seem to have that in mind during a contest ( Sarcasm unintended).
Always use fast input from now on and you'll never experience similar problems again.
Yup, I had some problems on SPOJ without Fast I/O, but then started using it everywhere. Even though my friends disapprove (for no apparent reason), I actually find it more convenient taking input just by writing 2 letters and the variable name :D
Just add Fast I/O to your standard template and you can focus on the problem!
That's not Fast IO. Is just normal IO.
C can be solved by treap and the asymptotic will be O(nlogn). This solution doesn't demand constrains on lengths and energy.
Can anyone Explain why this code give me WA on test case 8 ?! 11861412
how can I edit it?
thanks in advance.
Can anyone explain why this code 11861412 give me WA on test case 8 [problem B] ? and how can I repair it?
Maybe because you just checked if you could put "2 * qua" for boys. You didn't check if you could put "qua" for girls... That's the same mistake I've made... You have to check it because it could happen that you can put 2 * qua for boys, but the smallest cup doesn't support qua ml of water.
Problem E can be solved in O(n2) time. You can read my solution (11862688) if you interested in. (I've used that alphabet size is equal to 2, but it is easy to fix it)
The original solution can do o(n^2), since only n nodes will have more than one child.
Have you any time to debug my Error. Why my code gives wrong ans ? (http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11868836)
Please use fixed point precision printing. U can use
printf("%.10f\n",ans);to do thisHash can be used to find if a substring from index i to j is half palindrome or not.
Hash can be also used to find if a substring from i to j is half palindrome or not.
Well, I solved problem C a little differently.
First we sort the legs by their lengths in ascending order (the energy values don't matter). Then we split the sorted list into blocks, where the legs in the same block have the same length.
After that we iterate over every block. In iteration i, we try to find the answer when the legs in block i are the longest remaining.
In iteration i, obviously, all legs in block i must be kept in order to find the optimal answer. And we must remove all legs in blocks from i + 1 to block-count (since legs in block i are the longest remaining), and keep at most
block[i].size - 1legs in blocks from 1 to i — 1 (to keep the table stable). Therefore the answer equals tototal energy of block (i + 1)~block_count+total energy of block 1~(i - 1)—total energy of the (block[i].size - 1) largest elements in block 1~(i - 1).For the first and second part we can either use partial sums or calculate while iterating. For the third part, we can use a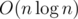 , I think?
, I think?
std::multisetto store all previous legs' energy values. For any k, the k largest elements can be accessed by just iterating k times in the multiset. Asymptotic time complexity is...My code (written rapidly during the contest and may not be so elegant): 11859771
Shouldn't this be subtracted total energy of the (block[i].size — 1) smallest energy elements in block 1~(i — 1) from total energy of block 1~(i — 1).
No, u r right. We should subtract total energy of block 1~(i — 1) — total energy of the (block[i].size — 1) largest elements in block 1~(i — 1)
Hi cyand1317, I think I used the same method as you with the difference that I used a priority queue to get the legs of highest energies from the legs of smaller sizes.
But for some reason I'm getting WA in case 8 and I cannot check why because it's very big. I get the correct result with all the cases where n < 30.
Could you please take a look at my code?
http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11870567
Hello. Glad that I can help. I'm taking a look at your code and here's what I've found so far.
There is a potential crash in this code. Try using a test case with n = 5 and length values
1 8 8 8 8. Whoa!This is because when your program scans the second block (with length = 8 and blocksize = 4), it tries to poll the blocksize - 1 = 3 largest elements in the previous blocks, which only has one element. Then
PriorityQueue.poll()returns null and causes the crash.However, this code still doesn't give correct answers after I fixed this bug (line #64, 11875986). I'll keep trying! (I ran into similar situations lots of times before and I'd really like to find an efficient way to get out of them :P)
Hello, thank you very much.
I fixed the problem, posted at the end of this thread and forgot to reply here.
The problem was not in the algorithm but in Java: http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/18943?#comment-239423
I'm happy that you've fixed it ;)
I am using a similar approach but i fail to comprehend why it is giving WA for the first test case while it is running fine on my system. Please check my comment for the approach. http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/18943?#comment-239449
My submission: 11875338
Rivx has explained why this code doesn't work the way you want. But after correcting these mistakes, it still gives incorrect answers. Perhaps the algorithm isn't that correct. I'll try to think about some ways to fix it.
Yes, it should be O(nlogn) as we access at max sum(k) elements in the multset and sum(k) is n.
Oh, yes, I didn't realize that! A clear explanation. Thanks :)
I have changed the type of array
c( 11867935 ) to long long and the code gets Accepted (11868444)! Can anyone explain why?Reading
doubletakes more time thanlong long(about twice I guess), for decimal points and many other things (such as expressions like 3.14e10) need to be checked. And n is relatively large.I'm wondering why this submission got TLE for problem B. I believe the complexity of this solution is also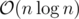 .
.
Taking double input is very time-consuming, and hence you need to use Fast Input/Output. Also, your code will get WA on test 32 if you do not use "cout.precision(x)", as cout as low precision by default. (Here x is greater than 6)
Changing to printf and scanf, here is your AC submission : http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11870036
Ah... thanks!
You're reading data too slow. Try to use scanf() instead of cin>>.
iostream is as fast (or even faster) than stdio, but by default it has special buffering enabled that makes sure that you don't get unexpected results when you use both cin and scanf. You can disable it by adding
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false)as the first line of your program (before any input/output operations).Also, if you alternate between cin and cout, it will flush output before each input operation (which is needed when cin and cout refer to the console, so the user sees the prompt before having to enter something), which can lead to very slow IO (common issue in problems where you need to answer lots of queries). This can be disabled with
std::cin.tie(nullptr).Thanks a lot!
Please improve the English translation
Can someone, please, tell me what's wrong with my code for C? It gives correct answer with all the small cases so I cannot debug it. At least some test case that won't pass with it.
I wrote a lot of comments to make it easy to understand: http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11870567
The idea is basically the same as the author:
Thank you very much in advance!
What happens if there aren't enough smaller legs? You loop from 1 to count-1, but the queue might not have enough elements in it. It crashes on the following test: 6 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1
It still doesn't pass test #8 with this fixed, though.
Thanks for checking. Yes, I noticed that just after posting but the corrected code below didn't pass 8 as you say :(
http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11870823
I cannot find a single case that doesn't work with my code. I'm running many random cases against Accepted codes without any luck :(
Finally, I found the problem with my code. It didn't have to do with the algorithm but with Java!
The problem was in the way that Java compares Integer objects:
Incorrect: if (legs[i].first != legs[i + 1].first) {
Correct: if (legs[i].first.intValue() != legs[i + 1].first.intValue())
Explanation: http://stackoverflow.com/a/1514919
AC code (almost the same): http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11873179
Writing your own class with two ints is faster, safer and more readable.
I agree, but it's probably not faster to code in a competition. My pair class is ready to sort by the first element and then by the second (the latter not needed in this case).
I guess it depends on how much I would use direct value comparison and how much coding time I'm expencting to save by not writing the class and comparator on the go.
Who can explain me why the compiler reterning wrong answer to this example:
500*3*71199.This will be 106798500, but it says that my programm reterns 106799000 even with this
if (n == 71199) cout << 500.0*71199.0*3.0 << endl;The submission: 11870868
The correct answer is:
106798500Your program print:
1.06799e+008what equal to106799000So you have less than 10^6 precision. To have ACC you must writecout << fixed << setprecision(10) << answer << endl;can you please provide codes ?
In second question B --> we can do without binary search ie just be greedy :)
We can even do it more simplified as let say g=a[1] and b=a[n+1] (after sorting 1 based index) then just have 2 conditions if tc = (b*0.5*n+b*n) --> b*0.5 maximum girl cup can have condition being b*0.5 <=g if not so then directly (g*n+2*g*n) is the answer. for case when ans>w take ans=w. that's it :) Here's my AC code — http://ideone.com/1POnoF
http://paste.ubuntu.com/11801550/
I'm getting TLE in E problem. i have a matrix named pal. pal[i][j] = 1 means substring that starting from i and length is j is half palindrom.
i calculate matrix with complexity n^2 and then i find what string is.
i do that with three vector. i wont explain more. i think code is clear.
but the problem is why i am getting TLE ? can anyone tell ?
Can anyone help ?
I solved C in O (N log N ). Here is the algo :
1) In a multi set (or any bst like structure) , store all the legs with their energies as < length, energy >, call this as M. Let total weight of all legs be TOT.
2) For all distinct lengths in this map , assume that the table is going to be built with this length as maximum length, call this length L. Let there be total of CNT number of these legs with length L. Now what you need to find is CNT-1 legs with max energy and length less than L. This can be done using a multiset for energies — once you have crossed a length, you insert all the different energies for this length into it, call this multi set as W.
3) Find the net energy value of all legs of this table = ET and update answer with ans = min(ans,TOT-ET).
Complexity analysis : 1) Creation of M = O (N log N)
2) Finding CNT for all distinct lengths — O(N)
3) Creation of W = O(N log N)
4) Selecting CNT — 1 legs of max weight from W = O (N)
Because worst case, we can have sqrt N distinct lengths occuring sqrt N times and so we will have to go through sqrt N max energy legs for each of the sqrt n lengths = O(sqrt n * sqrt n) = O(n)
Soln link — http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11872727
PS : During contest, in the last while loop, I wrote "it1" as "it" and unfortunately "it" was also a variable in that scope so that caused WA on some pretest. Silly typo :\
I am new here. What should I do if I cant understand the solutions even after reading the editorials? Any tips?
You can take a look at others' code, which you can find by clicking the numbers like 'x2917' on the 'PROBLEMS' page. If you don't know an algorithm mentioned in the editorial, search for it on the Internet. If these still don't help, directly commenting under the editorial asking for help is another way. When doing this, details such as which problem and where you didn't understand (or even better, which sentence) are necessary.
fcspartakm, I understand both solutions, greedy and bs, but I always had a doubt in binary search with limits of type double. Can you give any tips, did not submit to the binary search but understood perfectly, the only question is in the loop breaks.
For example:
l=min of search, r=max of search, EPS=1e-6how shall I compare them to complete the search? so?l-r<EPSI wanted to know, as they do this test? or rather, what better way to do it?
r-l<EPSsincer>lDon't compare doubles, use fixed number of iterations. I believe 64 should be enough in all cases.
Also, in this particular problem, answer can be only integer or (integer + 0.5). So you can multiply everything by 2 and get rid of floating-point numbers at all.
Thanks for the interesting problems :)
For Problem C Can anyone please let me know why i am getting WA for the first test case while the code is running fine on my system atleast for the first three cases.11875338
I am maintaining a set for the table lengths'(st) and another set to store the energy levels for a particular length(pq[]). The array cnt[] stores the number of occurrences for a particular length.
The loop basically tests for three possibilities.
->set::iterator it,
->pq[*it]
->cnt[*it] Are they not contradicting? I don't know but can you use iterators of different types invariably?
*itdereferences the iterator, so it's simply an int. However, st.end() is NOT the iterator for the last element — it actually points beyond the end of the set, so you can't dereference it. You need to decrement it by one (--st.end()). In other containers like a vector you can useback(), but there is no such method in a set.However, that block isn't reached in the first test case anyway. You didn't initialize
mini, so if it starts out as zero in GCC, you will get zero as your answer. In VS it starts out as -858993460, which is even worse.Задачу С думал так же решать,как и в разборе,но испугался ограничений на время (1с). Подскажите, каким образом решение O(n*d+n*logn) может пройти на Free Pascal за 1с? Насколько мне известно (опыт+инфа) 10^6 итераций ~1 сек.
Какой-то странный у тебя опыт (инфа)
На Сodeforces достаточно хорошие машины, и решение за 10^8, иногда даже 10^9 но с маленькой константой отлично заходят на ура. Да и вообще на любых олимпиадах 1 секунду можно расценивать как 10^7-10^8, исключение — медленные языки программирования.
Спасибо. Просто давно интересовался временем работы. Я,кроме Pascal,больше не пишу ни на чем. А на Pascal решения видимо работают много медленнее
After I read the editorial, problem A is much easier than I think :((
Thanks for the editorial. First problem could also be solved with complexity o(max(max1-min1,max2-min2,max3-min3)). My friend submitted using this method and got accepted. But since we can solve it with o(1) like in the editorial I think that solution is kinda slow.
Now we need to use dfs and try to split every component in two part
Can someone explain this part of problem D?
Use DFS to try to color the graph in two colors (so that no edge connects two vertices of the same color). That is, initially the graph is uncolored, and you do something like this:
he want to say that if component isnt bipartite (means we cant split it), it already has odd cycle.
read what bipartite graph is. http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bipartite-graph/
In 557B — Pasha and Tea party what is "lf" and "rg"?
Binary search boundaries (the range in which we know the answer should be).
lfis initially 0, andrgis initiallyw. On every iteration, we split the range into two halves, and choose which one of them is correct. Eventually the range will become small enough that we can print the answer.I implemented following: lf=0 rg=w/3*n While(lf<rf) { mid=(lf+rg)/2; if(mid<= a[0] && mid*2 <= a[n]) lf=mid Else rg=mid }
wheree a is sorted array of cup capacity And this loop doesn't terminate.
Always use fixed number of iterations in binary search on doubles. I usually use 150-200 iterations and everything works.
Does it work for all cases irrespective of size of input? BTW is my implementation correct apart from correction you suggested?
If you can represent left and right bounds using doubles — than the answer is yes, but I don't remember the reasoning of this. Maybe someone can elaborate this?
rg=w/(3*n)— you should use parenthesis here150-200 is a way too much, considering doubles only have 52 significant bits. Unless the interval converges to zero, the last 100-150 iterations will do nothing.
In fact, you can do
while (x != y)and it will do 50-60 iterations in most cases — except when the answer is zero, in which case it can do about a 1000 iterations. Of course, you shouldn't do that because you're likely to run into the same problem as with int binsearch — when x and y are the closest possible numbers, (x+y)/2 will be equal to either x or y, and if you guess "incorrectly", you will get an infinite loop. You could fix it by using std::nextafter (i.e. if you know that the answer for m is no, then technically you need to set y to the number just below m, orstd::nextafter(m, l)), but that's not pretty.Not to mention that this problem doesn't need binary search anyway :(
You have mistake in Problem A: Not <=, it will be right if write >= !
Why doesn't the tutorial appear with the problem statements? Would I always have to navigate to the blog to see the editorial? How come some contests have tutorials appearing with each problem statement?
Not sure what you mean, after each contest the blog entry is updated with a link to the editorial. You can see all entries for the recent contests on the front page.
There is "→Contest materials" tab at the right bottom corner of contest interface. Usually there is a link to tutorial(if anyone added it)
Why TLE O (700) ? 11885455
UPD: because of double with cin :( 11885605
For 557C, we can use the same idea to find the solution without too much thing to compute.
The idea is (reiterating author's approach): Let's say we want to keep legs with length k. All legs length greater than k must be removed (otherwise k is not the maximum), the remaining is to make sure removal of legs length less than k requires minimal energy.
Observation: If there are P legs whose lengths are less than k, and there are Q legs with length k. You need to remove at least P - Q + 1 legs whose lengths are less than k to make the table stable.
Observation: By above, you need to keep at most Q - 1 legs whose lengths are less than k to make the table stable. Otherwise, there are at least Q non k-legs with Q k-legs, and k-legs is obviously not the majority. Table is not stable.
Observation: Remove legs with minimal energy is equivalent to keep legs with maximal energy.
So, you need to compute two things: total energy to remove (now means keep) k-legs, number of k-legs. Enumerate all possible maximal k, get the keep energy for k-legs, plus get the sum of the largest Q - 1 energies of legs whose length is less than k. The way to do it is similar to the O(nd) approach described by author, but we take the exact opposite values. Find the maximum values among all choices of k, get the answer by total energy — this max energy.
Doing so does not require suffix sum.
We check at a node if sum[toa] <= k.
Let us say sum[toa] is less than or equal to k. Then we go to node toa, now, for all nodes sum[toa from new node] will also always be less than k.
So, in such a case k will never become less than or equal to zero.
The how will the algorithm terminate?
Typo, it should be sum[toa] >= k
There is one more missing thing. Once we reach a particular node $$$v$$$ while constructing the answer, we must also subtract $$$cnt[v]$$$ from $$$k$$$ to account for half-palindromes ending at the node $$$v$$$. So, if $$$sum[to_a] \ge k$$$, we move towards $$$to_a$$$ and also update $$$k$$$ as $$$ k$$$ $$$-= cnt[to_a]$$$. Otherwise, we move towards $$$to_b$$$ and update $$$k$$$ as $$$k$$$ $$$-= (sum[to_a] + cnt[to_b])$$$
I found the statement of the Problem A to be not clear. I could not understand the fact that if we already have max possible A diplomas, then try finding max possible B diplomas and further max possible C diplomas.
My solution is a bit different from the author' solution:
11892821
Call
t1,t2,t3is the number of diplomas in first, second and third degree in the optimal answer. We know thatt1+t2+t3 = n.Our goal is to maximize
t1first, then maximizet2. So we will first maket1as large as possible. We knew that 't1 <= max1'. However, we'll need to take care about the fact thatt2 >= min2andt3 >= min3, too. So, we'll haven-t1 = t2+t3 >= min2+min3, which meant1 <= n-min2-min3. Finally, we'll havet1 = min(max1, n-min2-min3).At this point, we'll have
n := n-t1diplomas left. Now, we will take do the similar thing again, maket2as large as possible. We know thatt2 <= max2andt3 >= min3<=>n-t2 >= min3<=>t2 <= n-min3. So we'll havet2 = min(max2, n-min3).We now know the value of
t1andt2, so we also get the value oft3, which equaln-t1-t2.For Problem D of the contest I have implemented the idea of DFS mentioned in the Editorial but i am still getting WA on the test 31. http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/11901124 I would be grateful if anyone could point out my mistake and point me in the right direction.
I think this line contains a mistake. A path between a black and white vertices is of odd length (a cycle is of even length), is it not?
To solve B, I just needed to sort them and write only 2 lines and it's done, no need to iterate on any thing, the answer pops right up. My solution: 11927301 Complexity: O(n.log(n)) for the sorting
I was tricked by myself when I attempted to solve D.
The definition of odd cycle is obvious: Any graph that is not bi-colorable iff it has odd cycle (proof omitted). So if the graph has odd cycle it's done, we don't need to add any edge and this is the only way to achieve minimum (thus
0 1). Note that bicolorable graph is bipartite.The solution remains to categorize answers for different class of bipartite graph. Note that you need at most 3 edges to form an odd cycle in any cases, so just think about when you need to answer 1, 2, and 3.
Case 1: when minimum = 3. It means you need to form a triangle by picking three vertices. This also means that there are no edges, thus maximum vertex degree = 0. In this case, answer is to pick any three vertices, which is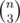 .
.
Case 2: when minimum = 2. It means that no vertex has at least two edges (otherwise minimum = 1 by joining two vertices from the two edges to form a triangle). Which implies that maximum vertex degree = 1. To form a triangle, we must use any of such edge (u, v) and find other vertex w and use two edges to form a triangle. Note that since maximum degree = 1, all m edges are the required edge. So the answer is m × (n - 2) (for each edge, pick other vertices to form triangle).
Case 3: when minimum = 1. This means that maximum degree is at least 2. This is also where I got tricked. In this case, we don't just want to count number of ways to form triangle, since one can add an edge to form an odd cycle. Consider this: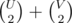 .
.
W-B-W-B-W, whereWmeans a white vertex,Bmeans a black vertex. One can add just on edge, that connects the first and the lastW, to form an odd cycle with length 5. Given this, the answer is much simpler: notice that for any connected bipartite graph, connecting any two vertices of the same side breaks bipartite-ness, thus odd cycle exists. So the answer is simple: for each bipartite connected components, the answer for that component is the number of way to connect two vertices on the same side. Suppose the bipartite graph has U vertices on the left, V vertices on the right, the answer isIndeed, what if the problem is like: find the minimum number of edge added to form a triangle, and how many ways to do. When the graph is not bipartite, I think it requires matrix multiplication. If the graph is bipartite, the answer remains the same when the minimum edge added is 3 or 2. When minimum edge added is 1, I can't come up of anything that is faster than O(n2).
We can use dp for checking half-palindromes.
Suppose our good[][] array works correctly for substrings of length 1,2,3...i-1 Now we have to consider the substrings of length i and update the good[][] array.
It's obvious that good[i][j] = 1 if and only if,
- char at position i equals char at position j and
- (i+2 > j-2) or (dp[i+2][j-2] == 1)
Link
Ребят, я новичок, у меня возникли трудности по задаче B, не совсем понимаю, как реализовать бинарный поиск с итерациями в данном случае, не мог бы кто-нибудь показать код программы по аналогии с алгоритмом, приведенным выше. C++ или Паскаль (желательно паскаль)
Hi, Im beginner and i have any problems in 557B. I dont understand how to realize this example, exactly this example. I want to see code for this algorithm, с++ or Pascal (desirable Pascal), sorry for my very bad English
Привет, в этой задаче бинпоиском нужно искать ответ, если он слишком большой, то сдвинем правую границу, иначе левую. Также стоит отметить, что поиск у нас вещественный, и чтобы не было проблем с точностью вместо условия в while(r — l > eps), где eps = 10^-7, проделываем итерации 1000 раз, while(q > 0), где q = 1000. Вот отрывок кода на c++. d — минимальная чашка у девочек, m1 — минимальная чашка у мальчиков, w — сколько всего чая в чайнике.
Не слишком ли много итераций?
Разве 1000000 — это много? Можно и меньше, решил перестраховаться.
Ну 100 Итераций вполне достаточно.
I think the solution of problem A is probably wrong.
Like for the first condition max1 + min2 + min3 ≤ n, which means n - min2 - min3 ≥ max1.
And it saids the optimal solution is (n - min2 - min3, min2, min3), which actually invalid.
Yes, it seems the less and equal symbol should be replaced by large and equal symbol. Can author fcspartakm have it a look? :)
I have a O(N^2 + N^2 log N + N^2) solution for problem E.
Firstly, finding all the half-palindromes by O(N^2) brute-force. Then, sorting all the suffix by their indices with O(N log N) algorithm. In fact, it can be optimized by using suffix array algorithm, and this will come up with an totally O(N^2) algorithm for this problem. Finally, sweeping the suffixes for counting the k-th sub-string in O(N^2).
And this is not depended on the number of kinds of alphas in the string. :) I don't know if my solution is strictly right, so comments are welcome. 11894668
"Sweeping the suffixes for counting the k-th sub-string in O(N^2)"-could you explain this part?
Can anyone, please, explain Problem E ?
With all due respect, the explanation offered in this editorial is not clear at all.
I understand the part where we determine which substrings are half-palindromes as I did myself but I don't get the part where I'd have to use a trie. I tried to use a trie by myself but I think it's O(n3) .
It would be really nice if someone explains the approach of this editorial!
How to solve C if 1 < = di < = 105?
I don`t know how that collocation will be in English, but you can compression the coordinates. I think you understand me.(does it work?)
Can anybody give the the idea of Div 2 C, when the range of di can be anything and not just 1 ≤ di ≤ 200
My approach have time complexity is O(N(logN)2), which not depend on value of di.
First of all, I sort the array with depend in l[i]. Second, sort the array with depend on d[i]. Now for each leg, we know the ordinal of their energy units. For example, in test case 3, our sorted array (called a[]) and the ordinal of their energy units (called c[]):
So we now, for the $i$-th leg, we have greedy approach: If we choose to use this leg, then we will use
all of the legs that have the same value of lengthwith this chosen leg. Call the number of legs that have the same length with i-th leg is k. The enery when we chose i-th leg is sum enery units of all the leg have greater length and sum of the i - (2k - 1) smallest enery units leg of which length is strictly smaller than i-th leg.Because all table must have more than a half legs of greatest length, so is we choose i-th leg is greatest length, the maximal numbers of legs that a table could have is 2k - 1 legs. To make i-th leg is the greatest length's leg, then we need to remove all the legs have greater length and take no more than k - 1 legs have smaller length. At the moment, we have i legs with have not greater than i leg, so greedily, we just need to remove i - (2k - 1) legs that have smallest enery units.
Now, for each leg, we could easily use prefix sum to find sum of all the legs have greater length than our chosen leg's length. However, the harder problem is find the sum of i - (2k - 1) smallest leg's enery units. Remember about the array c[], which we store the ordinal number of the leg's enery units. Now, after attempt the i-th leg, we will knows that it exist the c[i]-th smallest enery units value.
For example, when we check the 4-th leg (base on array a[]), we will have these valid enery units values [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]. As we want to find sum of i - (2k - 1) = 4 - (2 * 2 - 1) = 1 smallest value, so we will find sum of 1-th smallest enery units, in this case is 3.
Also notice that, the numbers of valid enery units values from 1 to j is always not less than the numbers of valid enery units values from 1 to i which i > j. So we could use binary seach to find the smaller number x that from 1 to x we can find i - (2k - 1) valid value. To do each of this operation in O(logN), we could use Fenwich or Segment Tree. After found the result x, our answer in case we use the i-th leg is
sumLengthSmallestValidValue(1, x)+sumLength(i+1, n).In the other hand, to make sure that we just find the sum of the smallest enery units legs which have length strictly less than our chosen leg's length,
after we check all the same length legs, then we update, not update for each leg(we could use stack or queue to solve that — if the i-th leg is diffence than the i - 1-th leg, than we update all the legs that stored in the queue now, other wise, if the i-th leg is same as the i - 1-th leg, push i to the queue).Here is my code which uses Segment tree: 23901663. So the time complexity is O(N(logN)2) due to using
binary search on Segment treefor each leg. This is the first time I write the solution, so sorry for my bad idea's expression. Feel free for asking me any question, I will trying my best to explain :D.Wow, so detail, thanks to your solution.
can you please tell me why my solution is getting WA on 13th tc. http://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/31828130. thanks.
In the guide of 557A, comparison symbols of the first two conditions seem wrong. '<=' should be replaced with '>=' i guess.
The editorial for the first problem is wrong and it is weird that no one has pointed it out.
Problem C — Arthur and table can be solved in O(n*logn*logn) using fenwick tree, so even if difference in maximal and minimal energy is large,the solution will pass.
Here's my submission link : https://codeforces.com/contest/557/submission/92999357
in problem b (Pasha and Tea) i used binary search to solve problem but in this solution it get TLE but this solution accepts ,i used 10**-10 as epsilon in first solution and 10**-6 as epsilon in second solution . can someone explain why this happen in two epsilon please??
in problem B, i used binary search but in first solution it get TLE and it use 10**-10 as epsilon.
in second solution it accepts and it use 10**-6 as epsilon , can any one explain this two cases with different epsilon??
If in Question B I take the value for x as min(w/3n,a[0],a[n]/2){where a is sorted} then that shall be enough to get the maximum allowable x right..?
This approach failed on tc32 and I am unable to see why could someone please help me with this...